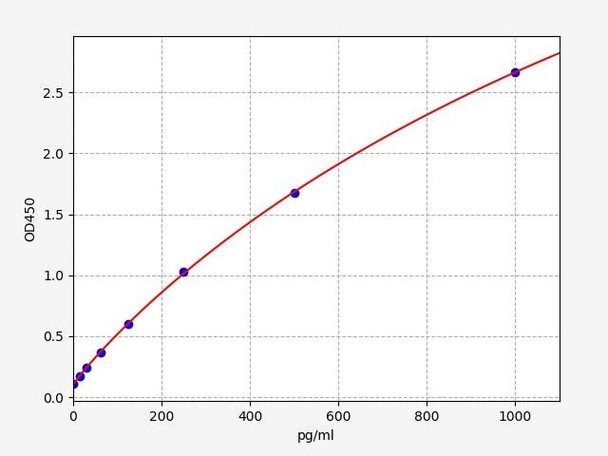
Description
Human BDG ELISA
Beta-D-glucan (BDG) is a major component of the cell wall of pathogenic fungi and yeast, such as Candida albicans. BDG is used as an infection biomarker, allowing for the detection of systemic infection. The Assay Genie Human BDG ELISA allows for the quantitative determination of BDG concentrations in serum plasma and other biological fluids.
Key Features
| Save Time | Pre-coated 96 well plate | |
| Quick Start | Kit includes all necessary reagents | |
| Publication Ready | Reproducible and reliable results |
Overview
| Product Name: | Human BDG ELISA Kit |
| Product Code: | HUFI01365 |
| Size: | 96 Assays |
| Alias: | beta-D-glucan |
| Detection Method: | Sandwich ELISA, Double Antibody |
| Application: | Quantitative determination of Human BDG concentrations in serum plasma and other biological fluids |
| Sensitivity: | 9.375pg/ml |
| Range: | 15.625-1000pg/ml |
| Storage: | 4°C for 6 months |
| Note: | For Research Use Only |
Additional Information
| Recovery: | Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of Human BDG and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Human BDG in samples.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Linearity: | The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Human BDG and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| CV(%): | Intra-Assay: CV<8% |
Kit Components
| Component | Quantity | Storage |
| ELISA Microplate (Dismountable) | 8x12 strips | 4°C for 6 months |
| Lyophilized Standard | 2 | 4°C/ -20°C |
| Sample/Standard Dlution Buffer | 20ml | 4°C |
| Biotin-labeled Antibody (Concentrated) | 120ul | 4°C (Protection from light) |
| Antibody Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| HRP-Streptavidin Conjugate (SABC) | 120ul | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| SABC Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| TMB Substrate | 10ml | 4°C (Protection from light) |
| Stop Solution | 10ml | 4°C |
| Wash Buffer (25X) | 30ml | 4°C |
| Plate Sealer | 5 | - |
Other materials required:
- Microplate reader with 450 nm wavelength filter
- Multichannel Pipette, Pipette, microcentrifuge tubes and disposable pipette tips
- Incubator
- Deionized or distilled water
- Absorbent paper
- Buffer resevoir
Protocol
*Note: Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the exact instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
Before adding to wells, equilibrate the SABC working solution and TMB substrate for at least 30 min at 37°C. When diluting samples and reagents, they must be mixed completely and evenly. It is recommended to plot a standard curve for each test.
| Step | Procedure |
| 1. | Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate respectively, and then, record their positions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Wash plate 2 times before adding standard, sample and control (zero) wells! |
| 2. | Aliquot 0.1ml standard solutions into the standard wells. |
| 3. | Add 0.1 ml of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well. |
| 4. | Add 0.1 ml of properly diluted sample ( Human serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and other biological fluids.) into test sample wells. |
| 5. | Seal the plate with a cover and incubate at 37 °C for 90 min. |
| 6. | Remove the cover and discard the plate content, clap the plate on the absorbent filter papers or other absorbent material. Do NOT let the wells completely dry at any time. Wash plate X2. |
| 7. | Add 0.1 ml of Biotin- detection antibody working solution into the above wells (standard, test sample & zero wells). Add the solution at the bottom of each well without touching the side wall. |
| 8. | Seal the plate with a cover and incubate at 37°C for 60 min. |
| 9. | Remove the cover, and wash plate 3 times with Wash buffer. Let wash buffer rest in wells for 1 min between each wash. |
| 10. | Add 0.1 ml of SABC working solution into each well, cover the plate and incubate at 37°C for 30 min. |
| 11. | Remove the cover and wash plate 5 times with Wash buffer, and each time let the wash buffer stay in the wells for 1-2 min. |
| 12. | Add 90 µl of TMB substrate into each well, cover the plate and incubate at 37°C in dark within 10-20 min. (Note: This incubation time is for reference use only, the optimal time should be determined by end user.) And the shades of blue can be seen in the first 3-4 wells (with most concentrated standard solutions), the other wells show no obvious color. |
| 13. | Add 50 µl of Stop solution into each well and mix thoroughly. The color changes into yellow immediately. |
| 14. | Read the O.D. absorbance at 450 nm in a microplate reader immediately after adding the stop solution. |
Sample Type
When carrying out an ELISA assay it is important to prepare your samples in order to achieve the best possible results. Below we have a list of procedures for the preparation of samples for different sample types.
| Sample Type | Protocol |
| Serum | If using serum separator tubes, allow samples to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Collect the serum fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. If serum separator tubes are not being used, allow samples to clot overnight at 2-8°C. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Remove serum and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Plasma | Collect plasma using EDTA or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge samples at 4°C for 15 mins at 1000 × g within 30 mins of collection. Collect the plasma fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Note: Over haemolysed samples are not suitable for use with this kit. |
| Urine & Cerebrospinal Fluid | Collect the urine (mid-stream) in a sterile container, centrifuge for 20 mins at 2000-3000 rpm. Remove supernatant and assay immediately. If any precipitation is detected, repeat the centrifugation step. A similar protocol can be used for cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Cell culture supernatant | Collect the cell culture media by pipette, followed by centrifugation at 4°C for 20 mins at 1500 rpm. Collect the clear supernatant and assay immediately. |
| Cell lysates | Solubilize cells in lysis buffer and allow to sit on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge tubes at 14,000 x g for 5 minutes to remove insoluble material. Aliquot the supernatant into a new tube and discard the remaining whole cell extract. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Tissue homogenates | The preparation of tissue homogenates will vary depending upon tissue type. Rinse tissue with 1X PBS to remove excess blood & homogenize in 20ml of 1X PBS (including protease inhibitors) and store overnight at ≤ -20°C. Two freeze-thaw cycles are required to break the cell membranes. To further disrupt the cell membranes you can sonicate the samples. Centrifuge homogenates for 5 mins at 5000xg. Remove the supernatant and assay immediately or aliquot and store at -20°C or -80°C. |
| Tissue lysates | Rinse tissue with PBS, cut into 1-2 mm pieces, and homogenize with a tissue homogenizer in PBS. Add an equal volume of RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors and lyse tissues at room temperature for 30 minutes with gentle agitation. Centrifuge to remove debris. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C |
| Breast Milk | Collect milk samples and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 60 min at 4°C. Aliquot the supernatant and assay. For long term use, store samples at -80°C. Minimize freeze/thaw cycles. |
BDG Background
Beta-D-glucan (BDG) is a polysaccharide that plays various roles in fungal biology and has gained significance as a biomarker for fungal infections. Found in the cell walls of fungi, BDG serves structural and protective functions while also acting as a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) that triggers immune responses.
BDG Structure and Function
BDG is composed of glucose units linked by beta-glycosidic bonds. It forms a complex and highly organized network within the fungal cell wall, providing rigidity and structural integrity. Additionally, BDG acts as a shield against environmental stresses, such as osmotic pressure and enzymatic degradation. The presence of BDG in the fungal cell wall also influences fungal cell recognition and interaction with the host immune system.
BDG Immunological Significance
BDG functions as a PAMP, activating the immune system through interactions with pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) on immune cells. The binding of BDG to PRRs, such as Dectin-1, triggers a cascade of immune responses, including the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and activation of phagocytosis. This immune activation is vital in combating fungal infections and shaping the host defense response.
BDG FAQs
What is the BDG ELISA Kit?
The Human BDG / beta-D-glucan ELISA Kit is a laboratory tool for quantifying beta-D-glucan levels in human biological samples.
What are the advantages of using the BDG ELISA Kit?
The Human BDG / beta-D-glucan ELISA Kit provides a highly specific and sensitive method for quantifying BDG in biological samples. It offers a user-friendly protocol and allows researchers to obtain precise measurements.
Where can I find more information about the BDG ELISA Kit?
For more detailed information about the BDG ELISA Kit, including technical specifications, performance characteristics, and ordering details, please refer to the product brochure or contact our customer support team. We are here to assist you with any inquiries you may have.