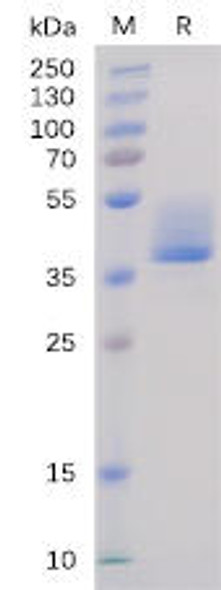
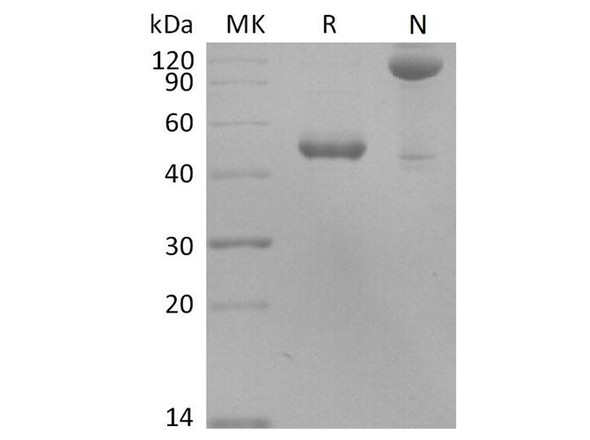
Description
| Product Name: | Human BAFF R Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB0087 |
| Size: | 50µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | BAFF R |
| Synonyms: | TNFRSF13C, CD268, BAFF-R, MGC138235, B cell-activating factor receptor. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.2?m filtered concentrated (1.0mg/ml) solution in 20mM PB, pH 8.0, 500mM NaCl. |
| Solubility: | It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized B Lymphocyte Stimulator Receptor Recombinant in sterile 18M?-cm H2O not less than 100�g/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. |
| Stability: | Lyophilized BAFF-R although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution B Lymphocyte Stimulator Receptor should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C.Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity: | Greater than 95.0% as determined by:(a) Analysis by RP-HPLC.(b) Analysis by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MRRGPRSLRGRDAPAPTPCVPAECFDLLVRHCVACGLLRTPRPKPAGASSPAPRTALQPQESVGAGAGEAALPLPG |
| Biological Activity: | Determined by its ability to block BAFF induced mouse splenocyte survival. The expected ED50 for this effect is 1.0-5.0 �g/ml in the presence of 1.0�g/ml of human soluble BAFF. |
B cell-activating factor (BAFF) enhances B-cell survival in vitro and is a regulator of the peripheral B-cell population. Overexpression of Baff in mice results in mature B-cell hyperplasia and symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Also, some SLE patients have increased levels of BAFF in serum. Therefore, it has been proposed that abnormally high levels of BAFF may contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases by enhancing the survival of autoreactive B cells. The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for BAFF and is a type III transmembrane protein containing a single extracellular cysteine-rich domain. It is thought that this receptor is the principal receptor required for BAFF-mediated mature B-cell survival.
B Lymphocyte Stimulator Receptor Human Recombinant extracellular produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 76 amino acids and having a molecular mass of 7.7 kDa.The BAFF-R is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | BAFF-R: B-cell receptor specific for TNFSF13B/TALL1/BAFF/BLyS. Promotes the survival of mature B-cells and the B-cell response. Defects in TNFRSF13C are the cause of immunodeficiency common variable type 4 (CVID4); also called antibody deficiency due to BAFFR defect. CVID4 is a primary immunodeficiency characterized by antibody deficiency, hypogammaglobulinemia, recurrent bacterial infections and an inability to mount an antibody response to antigen. The defect results from a failure of B-cell differentiation and impaired secretion of immunoglobulins; the numbers of circulating B-cells is usually in the normal range, but can be low. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, integral; Cell cycle regulation; Receptor, misc.; Cell surface Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 22q13.1-q13.31 Cellular Component: integral to membrane; external side of plasma membrane Biological Process: B cell costimulation; B cell homeostasis; T cell costimulation; positive regulation of B cell proliferation; positive regulation of germinal center formation; positive regulation of T cell proliferation; positive regulation of interferon-gamma biosynthetic process Disease: Immunodeficiency, Common Variable, 2; Immunodeficiency, Common Variable, 4 |
| NCBI Summary: | B cell-activating factor (BAFF) enhances B-cell survival in vitro and is a regulator of the peripheral B-cell population. Overexpression of Baff in mice results in mature B-cell hyperplasia and symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Also, some SLE patients have increased levels of BAFF in serum. Therefore, it has been proposed that abnormally high levels of BAFF may contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases by enhancing the survival of autoreactive B cells. The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for BAFF and is a type III transmembrane protein containing a single extracellular cysteine-rich domain. It is thought that this receptor is the principal receptor required for BAFF-mediated mature B-cell survival. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q96RJ3 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 21264093 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 115650 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q96RJ3.1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q96RJ3 |
| Molecular Weight: | 18,935 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13C |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 13C |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | TNFRSF13C�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | BAFFR; CD268; CVID4; BAFF-R; BROMIX; prolixin�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13C; BAFF receptor; BLyS receptor 3; B cell-activating factor receptor; B-cell-activating factor receptor |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13C |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | B-cell-activating factor receptor; BAFF receptor; BAFF-R; BLyS receptor 3; CD_antigen: CD268 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | TNFRSF13C�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | TR13C_HUMAN |