Description
HEXA Monoclonal Antibody [PAT20F1A] (CPAB0176)
The HEXA Monoclonal Antibody (CPAB0176) is a highly specific antibody designed for research involving the HEXA protein, an enzyme that plays a key role in the lysosomal degradation of GM2 gangliosides. This antibody, produced in a monoclonal format, is highly reactive with human and mouse samples and is validated for use in various applications such as immunofluorescence and flow cytometry.HEXA, also known as beta-hexosaminidase A, is essential for the breakdown of GM2 gangliosides in lysosomes. Mutations in the HEXA gene lead to the accumulation of GM2 gangliosides, resulting in neurodegenerative disorders such as Tay-Sachs disease.
Research into the function and regulation of HEXA is crucial for understanding the pathogenesis of these disorders and developing therapeutic interventions.The HEXA Monoclonal Antibody (CPAB0176) offers researchers a reliable tool for studying the expression and localization of HEXA in various cell types and tissues. By targeting the HEXA protein, this antibody facilitates the investigation of lysosomal metabolism and the development of potential treatments for lysosomal storage disorders.
| Product Name: | HEXA Antibody |
| Product Sku: | CPAB0176 |
| Size: | 5μg |
| Host Species: | Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Anti-human HEXA mAb, clone PAT2F1A, is derived from hybridization of mouse F myeloma cells with spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized with a recombinant human HEXA protein 89-529 amino acids purified from Ecoli. |
| Clone: | PAT20F1A. |
| Reactivity: | Human |
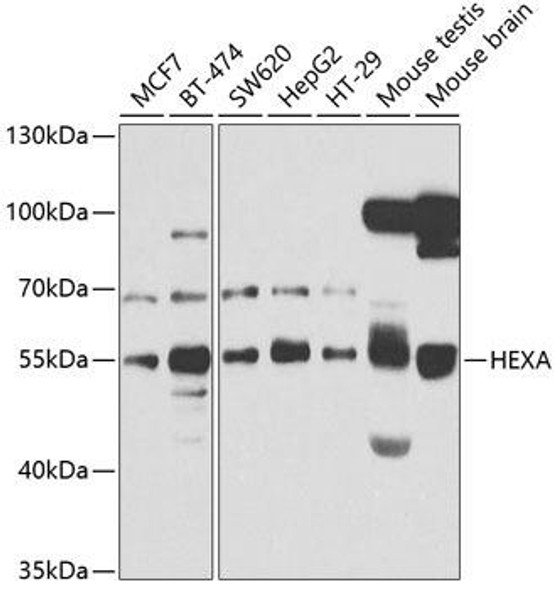
| Applications: | Western Blot, ELISA |
| Purification Method: | HEXA antibody was purified by protein-A affinity chromatography. |
| Isotype: | IgG2a |
| Background: | HEXA is the alpha subunit of the lysosomal enzyme beta-hexosaminidase which, combined with the cofactor GM2 activator protein, catalyzes the degradation of the ganglioside GM2, and other molecules having N-acetyl hexosamines terminus. The two subunits composing Beta-hexosaminidase, alpha and beta, belong to the glycosyl hydrolases family and are encoded by distinct genes. Alpha subunit gene mutations can cause Tay-Sachs disease (GM2-gangliosidosis type I). |
| Synonyms: | TSD, hexosaminidase A, Beta-hexosaminidase subunit alpha, Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase subunit alpha, Hexosaminidase subunit A, N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase subunit alpha. |
| Storage Buffer: | For periods up to 1 month store at 4°C, for longer periods of time, store at -20°C. Prevent freeze thaw cycles. |