Description
Heparanase 1 (CPAB0732)
The Heparanase 1 (HPA1) Polyclonal Antibody (CPAB0732) is a valuable tool for researchers studying heparanase 1, an enzyme that plays a key role in the remodeling of the extracellular matrix. This antibody has been raised in rabbits and is highly reactive with human samples, making it suitable for a variety of research applications.Heparanase 1 is known to be involved in various physiological and pathological processes, including tumor metastasis, inflammation, and angiogenesis. The HPA1 Polyclonal Antibody binds specifically to the heparanase 1 protein, allowing for the detection and analysis of this important enzyme in different cell types.
Research into heparanase 1 has shown its potential as a therapeutic target for cancer and other diseases where extracellular matrix remodeling is involved. This antibody can be used in studies related to cancer biology, inflammation, and various other research areas where heparanase 1 plays a role.Overall, the Heparanase 1 (HPA1) Polyclonal Antibody (CPAB0732) is a valuable tool for researchers investigating the function and therapeutic potential of heparanase 1 in various biological processes and disease states.
| Product Name: | Heparanase 1 (HPA1), Polyclonal |
| Product Sku: | CPAB0732 |
| Size: | 290μg |
| Host Species: | |
| Immunogen: | |
| Clone: | |
| Reactivity: | Other Polyclonal bodies |
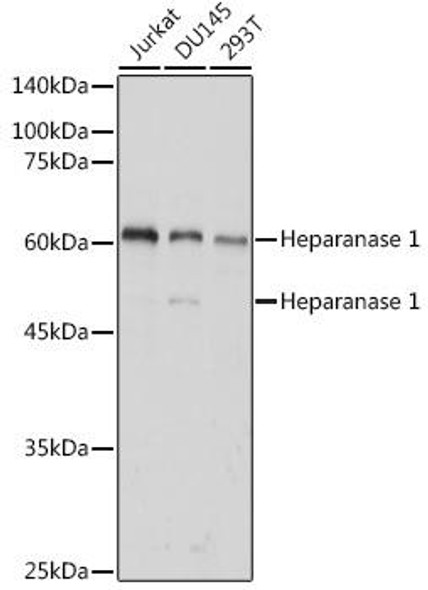
| Applications: | Western Blot, Immunohistochemistry |
| Purification Method: | |
| Isotype: | |
| Background: | Heparanase is an endo ß-D-glucuronidase, which degrades heparan sulfate side chains of heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) in the extracellular matrix. Heparanase plays an important role in ECM degradation, facilitating the migration and extravasation of tumor cells and inflammatory leukocytes (1,2,3). Upon degradation, heparanase releases growth factors and cytokines that stimulate cell proliferation and chemotaxis (4,5). Heparanase is a heterodimer comprised of a 50 kDa subunit harboring the active site and a 8 kDa subunit. It is produced as a latent 65 kDa precursor and proteolytically processed to its active form (1,6). Heparanase is highly expressed in myeloid leukocytes (i.e. neutrophils) in platelets and in human placenta. Human heparanase was found to be upregulated in various types of primary tumors, correlating in some cases with increased tumor invasiveness and vascularity and with poor prospective survival (7,8). |
| Synonyms: | |
| Storage Buffer: |