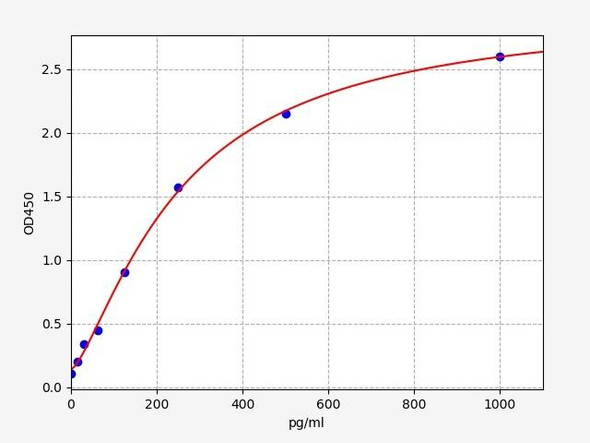
Description
GJB2 Antibody (PACO00626)
The GJB2 Polyclonal Antibody (PACO00626) is a powerful research tool designed for studies involving GJB2, a gap junction beta-2 protein known for its role in cell communication and hearing loss. This antibody, produced in rabbits, is highly specific for human samples and has been validated for use in Western blot applications.GJB2, also referred to as connexin-26, is a crucial component of gap junction channels that allow for direct communication between neighboring cells. Mutations in the GJB2 gene have been associated with various forms of deafness, making it a key target for research in the field of auditory biology and genetics.
By targeting the GJB2 protein, this antibody enables researchers to detect and analyze its expression in different cell types, providing valuable insights into its function and potential implications in hearing disorders. Its use in immunology and genetic studies makes it an essential tool for advancing our understanding of GJB2-related conditions and developing targeted therapies in the future.
| Antibody Name: | GJB2 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO00626 |
| Size: | 50ug |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, WB |
| Recommended Dilutions: | WB:1:500-1:2000 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen: | synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human Connexin-26. |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide. |
| Purification Method: | The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen. |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
| Synonyms: | GJB2; Gap junction beta-2 protein; Connexin-26; Cx26 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | GJB2: One gap junction consists of a cluster of closely packed pairs of transmembrane channels, the connexons, through which materials of low MW diffuse from one cell to a neighboring cell. Defects in GJB2 are the cause of deafness autosomal recessive type 1A (DFNB1A). DFNB1A is a form of sensorineural hearing loss. Sensorineural deafness results from damage to the neural receptors of the inner ear, the nerve pathways to the brain, or the area of the brain that receives sound information. Defects in GJB2 are the cause of deafness autosomal dominant type 3A (DFNA3A). Defects in GJB2 are a cause of Vohwinkel syndrome (VS). VS is an autosomal dominant disease characterized by hyperkeratosis, constriction on finger and toes and congenital deafness. Defects in GJB2 are a cause of palmoplantar keratoderma with deafness (PPKDFN). PPKDFN is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by the association of palmoplantar hyperkeratosis with progressive, bilateral, high-frequency, sensorineural deafness. Defects in GJB2 are a cause of keratitis-ichthyosis- deafness syndrome (KID syndrome); an autosomal dominant form of ectodermal dysplasia. Ectodermal dysplasias (EDs) constitute a heterogeneous group of developmental disorders affecting tissues of ectodermal origin. EDs are characterized by abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures such as hair, teeth, nails and sweat glands, with or without any additional clinical sign. Each combination of clinical features represents a different type of ectodermal dysplasia. KID syndrome is characterized by the association of hyperkeratotic skin lesions with vascularizing keratitis and profound sensorineural hearing loss. Clinical features include deafness, ichthyosis, photobia, absent or decreased eyebrows, sparse or absent scalp hair, decreased sweating and dysplastic finger and toenails. Defects in GJB2 are the cause of Bart-Pumphrey syndrome (BPS). BPS is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by sensorineural hearing loss, palmoplantar keratoderma, knuckle pads, and leukonychia, It shows considerable phenotypic variability. Defects in GJB2 are the cause of ichthyosis hystrix-like with deafness syndrome (HID syndrome). HID syndrome is an autosomal-dominant inherited keratinizing disorder characterized by sensorineural deafness and spiky hyperkeratosis affecting the entire skin. HID syndrome is considered to differ from the similar KID syndrome in the extent and time of occurrence of skin symptoms and the severity of the associated keratitis. Belongs to the connexin family. Beta-type (group I) subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Cell adhesion; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 13q11-q12 Cellular Component: connexon complex; ER-Golgi intermediate compartment; integral to membrane; plasma membrane; lateral plasma membrane Molecular Function:gap junction channel activity Biological Process: sensory perception of sound; gap junction assembly; cell-cell signaling; transport; male genitalia development; decidualization; response to progesterone stimulus; transmembrane transport; response to estradiol stimulus Disease: Deafness, Autosomal Recessive 1a; Ichthyosis, Hystrix-like, With Deafness; Deafness, X-linked 2; Deafness, Congenital, With Keratopachydermia And Constrictions Of Fingers And Toes; Keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness Syndrome, Autosomal Dominant; Knuckle Pads, Leukonychia, And Sensorineural Deafness; Keratoderma, Palmoplantar, With Deafness; Deafness, Autosomal Dominant 3a |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the gap junction protein family. The gap junctions were first characterized by electron microscopy as regionally specialized structures on plasma membranes of contacting adherent cells. These structures were shown to consist of cell-to-cell channels that facilitate the transfer of ions and small molecules between cells. The gap junction proteins, also known as connexins, purified from fractions of enriched gap junctions from different tissues differ. According to sequence similarities at the nucleotide and amino acid levels, the gap junction proteins are divided into two categories, alpha and beta. Mutations in this gene are responsible for as much as 50% of pre-lingual, recessive deafness. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P29033 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 77416855 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2706 |
| NCBI Accession: | P29033.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P29033,Q508A5, Q508A6, Q5YLL0, Q5YLL1, Q5YLL4, Q6IPV5 Q86U88, Q96AK0, Q9H536, Q9NNY4, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P29033 |
| Molecular Weight: | 26,215 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Gap junction beta-2 protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | gap junction protein, beta 2, 26kDa |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GJB2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HID; KID; PPK; CX26; DFNA3; DFNB1; NSRD1; DFNA3A; DFNB1A |
| NCBI Protein Information: | gap junction beta-2 protein; connexin 26; gap junction protein beta 2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Gap junction beta-2 protein |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Connexin-26; Cx26 |
| Protein Family: | Gap junction beta-2 protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GJB2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CXB2_HUMAN |