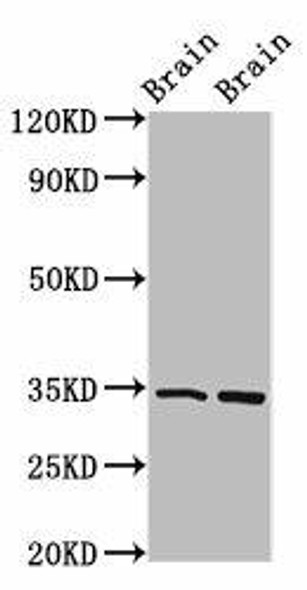
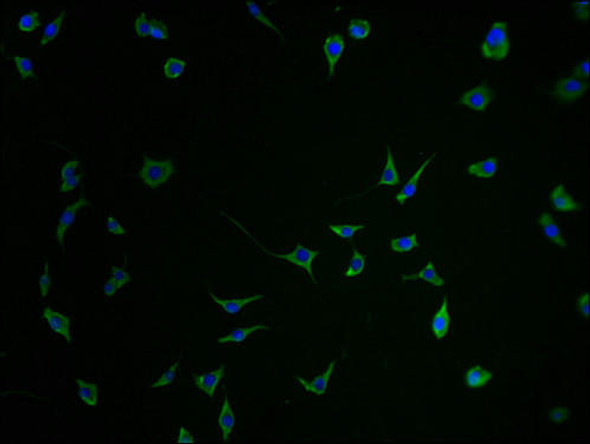
FOXE3 Antibody (PACO09335)
- SKU:
- PACO09335
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Applications:
- ELISA
- WB
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Conjugation:
- Unconjugated
Description
FOXE3 Antibody (PACO09335)
The FOXE3 Polyclonal Antibody (PACO09335) is specifically designed for research involving FOXE3, a transcription factor that plays a key role in eye development. This antibody, raised in rabbits, is highly reactive with human samples and is validated for use in various applications including Western blot and immunohistochemistry.FOXE3 is essential for the development of the lens and anterior segment of the eye, making it a crucial target for studying conditions related to eye development and function. Mutations in the FOXE3 gene have been associated with various eye disorders, making this antibody a valuable tool for research in ophthalmology and developmental biology.
By binding to the FOXE3 protein, this antibody enables researchers to detect and analyze FOXE3 expression in different cell types and tissues, providing insights into its role in eye development and related diseases. Understanding the function of FOXE3 is essential for advancing our knowledge of eye development processes and potentially developing new treatment strategies for eye disorders.
| Antibody Name: | FOXE3 Antibody (PACO09335) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO09335 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, WB |
| Recommended Dilutions: | |
| Species Reactivity: | Human |
| Immunogen: | Human FOXE3 |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | PBS with 0.02% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol, pH 7.3. -20°C, Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Purification Method: | Antigen Affinity purified |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
| Synonyms: | forkhead box E3;FOXE3;ASMD;FKHL12;FREAC8 ; |
| UniProt Protein Function: | FOXE3: Defects in FOXE3 are a cause of anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis (ASMD); also known as anterior segment ocular dysgenesis (ASOD). ASMD consists of a range of developmental defects in structures at the front of the eye, resulting from abnormal migration or differentiation of the neural crest derived mesenchymal cells that give rise to the cornea, iris, and other components of the anterior chamber during eye development. Mature anterior segment anomalies are associated with an increased risk of glaucoma and corneal opacity. Conditions falling within the phenotypic spectrum include aniridia, posterior embryotoxon, Axenfeld anomaly, Reiger anomaly/syndrome, Peters anomaly, and iridogoniodysgenesis. Defects in FOXE3 are a cause of congenital primary aphakia (CPA). Aphakia is a rare congenital eye disorder in which the lens is missing. It has been histologically subdivided into primary and secondary forms, in accordance with the severity of defects of the ocular tissues, whose development requires the initial presence of a lens. CPA results from an early developmental arrest, around the 4th-5th week of gestation in humans, that prevents the formation of any lens structure and leads to severe secondary ocular defects, including a complete aplasia of the anterior segment of the eye. In contrast, in secondary aphakic eyes, lens induction has occurred, and the lens vesicle has developed to some degree but finally has progressively resorbed perinatally, leading, therefore, to less-severe ocular defects. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p32 Cellular Component: nucleus; transcription factor complex Molecular Function:DNA binding; sequence-specific DNA binding; transcription factor activity Biological Process: anatomical structure morphogenesis; cell development; cell differentiation; lens development in camera-type eye; negative regulation of apoptosis; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter Disease: Anterior Segment Mesenchymal Dysgenesis; Aphakia, Congenital Primary |
| NCBI Summary: | This intronless gene belongs to the forkhead family of transcription factors, which is characterized by a distinct forkhead domain. The protein encoded functions as a lens-specific transcription factor and plays an important role in vertebrate lens formation. Mutations in this gene are associated with anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis and congenital primary aphakia. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | Q13461 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 12644406 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2301 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q13461.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q13461,Q5SVY9, Q9NQV9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q13461 |
| Molecular Weight: | 33,234 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Forkhead box protein E3 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | forkhead box E3 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FOXE3 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FKHL12; FREAC8 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | forkhead box protein E3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Forkhead box protein E3 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Forkhead-related protein FKHL12; Forkhead-related transcription factor 8; FREAC-8 |
| Protein Family: | Forkhead box protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FOXE3 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FOXE3_HUMAN |