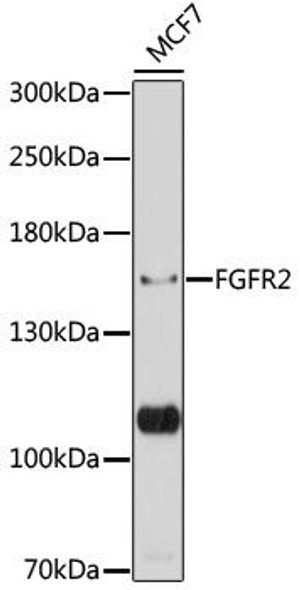
Description
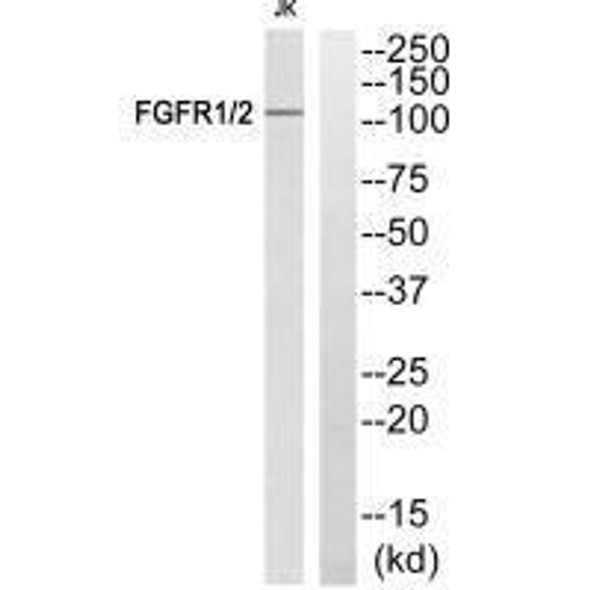
FGFR1/FGFR2 Antibody (PACO02718)
The FGFR1/FGFR2 Antibody (PACO02718) is a valuable tool for research involving fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs), key players in cell growth and development processes. This polyclonal antibody, derived from rabbits, exhibits high specificity and sensitivity in detecting FGFR1 and FGFR2 proteins in human samples, making it an essential component for Western blot applications.FGFR1 and FGFR2 are important receptors that mediate signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and migration. Dysregulation of FGFRs has been linked to various diseases, including cancer, skeletal disorders, and developmental abnormalities.
By targeting FGFR1 and FGFR2 with this antibody, researchers can gain valuable insights into the roles of these receptors in different cell types, contributing to advancements in cancer biology, stem cell research, and developmental biology. Overall, the FGFR1/FGFR2 Antibody (PACO02718) is a reliable tool for studying the functions and mechanisms of FGFR1 and FGFR2 in various physiological and pathological conditions, paving the way for the development of targeted therapies and diagnostic tools for FGFR-related diseases.
| Antibody Name: | FGFR1/FGFR2 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO02718 |
| Size: | 50ug |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, WB |
| Recommended Dilutions: | WB:1:500-1:2000 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen: | synthesized peptide derived from human Flg/Bek around the non-phosphorylation site of Y463/466. |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide. |
| Purification Method: | The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen. |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
| Synonyms: | FGFR1; BFGFR; CEK; FGFBR; FLG; FLT2; HBGFR; Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; FGFR-1; Basic fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; BFGFR; bFGF-R-1; Fms-like tyrosine kinase 2; FLT-2; N-sam; Proto-oncogene c-Fgr; CD antigen CD331; FGFR2; BE |
| UniProt Protein Function: | FGFR1: a receptor tyrosine kinase of the highly-conserved fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR). Binds both acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors and is involved in limb induction. Point mutations cause Pfeffer syndrome (finger and toe malformations and other skeletal errors) and dominant Kallmann syndrome 2. Stem cell leukemia lymphoma syndrome (SCLL) may be caused by a t(8;13)(p12;q12) translocation that fuses a zinc finger gene, ZNF198, to FGFR1. Various myeloproliferative disorders have been linked to translocations that fuse FGFR1 to FOP, FIM, CEP1 or the atypical kinase, Bcr. Inhibitor: SU5402. 20 isoforms of the human protein produced by alternative splicing have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, TK; Protein kinase, tyrosine (receptor); Oncoprotein; EC 2.7.10.1; Membrane protein, integral; Kinase, protein; TK group; FGFR family Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 8p11.23-p11.22 Cellular Component: integral to plasma membrane; cytoplasmic membrane-bound vesicle; extracellular region; plasma membrane; integral to membrane; nucleus; cytosol; receptor complex Molecular Function:heparin binding; identical protein binding; protein binding; fibroblast growth factor binding; protein homodimerization activity; fibroblast growth factor receptor activity; protein-tyrosine kinase activity; ATP binding Biological Process: paraxial mesoderm development; axon guidance; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; protein amino acid autophosphorylation; cell maturation; neuron migration; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; middle ear morphogenesis; protein amino acid phosphorylation; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity; sensory perception of sound; positive regulation of MAPKKK cascade; ureteric bud development; regulation of cell differentiation; induction of an organ; midbrain development; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation; positive regulation of cell proliferation; chondrocyte differentiation; angiogenesis; skeletal development; embryonic limb morphogenesis; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; inner ear morphogenesis; cell migration; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; phosphoinositide-mediated signaling; chordate embryonic development; transcription, DNA-dependent; in utero embryonic development; outer ear morphogenesis; MAPKKK cascade; positive regulation of cell cycle; neuroblast division in the ventricular zone; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase cascade; mesenchymal cell differentiation; skeletal morphogenesis; insulin receptor signaling pathway; auditory receptor cell development; innate immune response; positive regulation of neuron differentiation; regulation of lateral mesodermal cell fate specification Disease: Pfeiffer Syndrome; Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism 2 With Or Without Anosmia; Jackson-weiss Syndrome; Trigonocephaly 1; Osteoglophonic Dysplasia |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family, where amino acid sequence is highly conserved between members and throughout evolution. FGFR family members differ from one another in their ligand affinities and tissue distribution. A full-length representative protein consists of an extracellular region, composed of three immunoglobulin-like domains, a single hydrophobic membrane-spanning segment and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular portion of the protein interacts with fibroblast growth factors, setting in motion a cascade of downstream signals, ultimately influencing mitogenesis and differentiation. This particular family member binds both acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors and is involved in limb induction. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Pfeiffer syndrome, Jackson-Weiss syndrome, Antley-Bixler syndrome, osteoglophonic dysplasia, and autosomal dominant Kallmann syndrome 2. Chromosomal aberrations involving this gene are associated with stem cell myeloproliferative disorder and stem cell leukemia lymphoma syndrome. Alternatively spliced variants which encode different protein isoforms have been described; however, not all variants have been fully characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P11362 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 120046 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2260 |
| NCBI Accession: | P11362.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P11362,P17049, Q02063, Q02065, Q14306, Q14307, Q53H63 Q59H40, Q5BJG2, A8K6T9, A8K8V5, C1KBH8, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P11362 |
| Molecular Weight: | 91,868 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FGFR1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CEK; FLG; HH2; OGD; FLT2; KAL2; BFGFR; CD331; FGFBR; FLT-2; HBGFR; N-SAM; FGFR-1; HRTFDS; bFGF-R-1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; FGFR1/PLAG1 fusion; proto-oncogene c-Fgr; FMS-like tyrosine kinase 2; hydroxyaryl-protein kinase; fms-related tyrosine kinase 2; heparin-binding growth factor receptor; basic fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Basic fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; BFGFR; bFGF-R-1; Fms-like tyrosine kinase 2; FLT-2; N-sam; Proto-oncogene c-Fgr |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FGFR1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FGFR1_HUMAN |