Proteins
Recombinant Proteins
Designed for assays, drug discovery & more
Unlock reliable and high-quality recombinant proteins for your research. At Assay Genie, we provide a diverse selection of bioactive proteins, including cytokines, growth factors, CD markers, and viral proteins across multiple species and research areas.

Validation Data

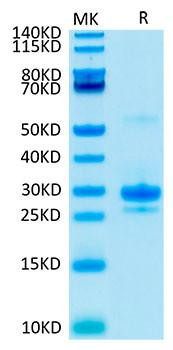
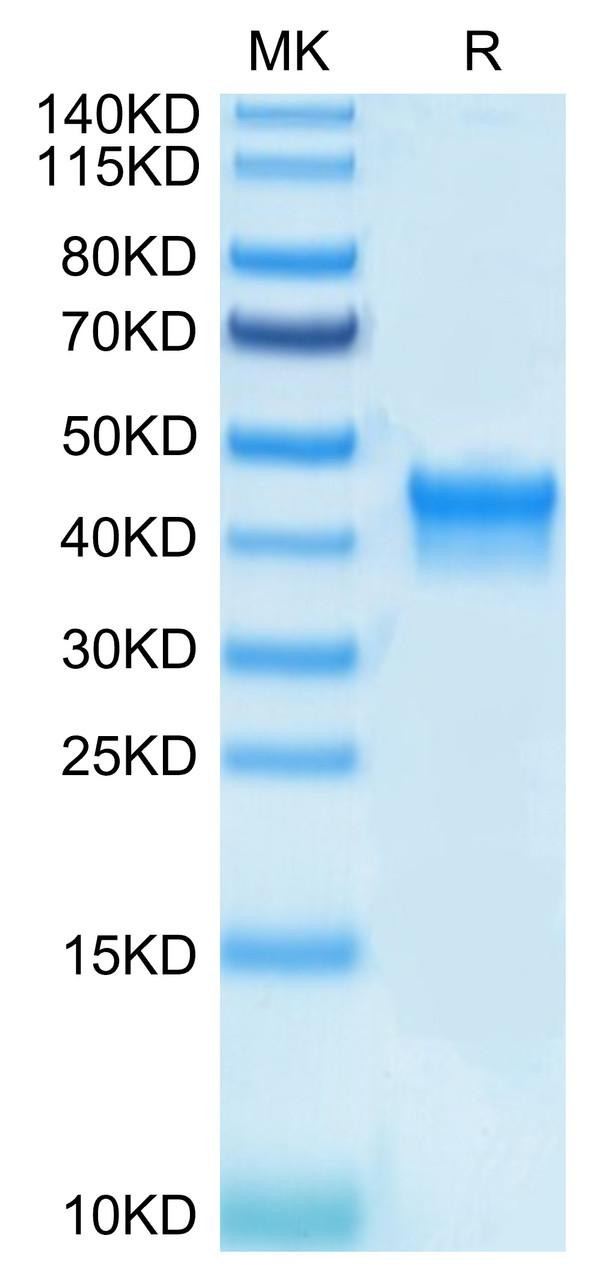
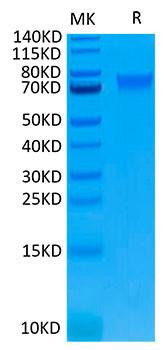
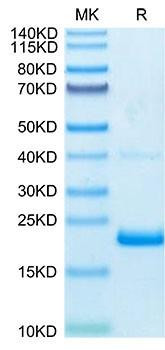
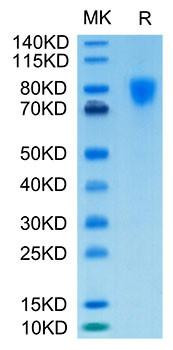
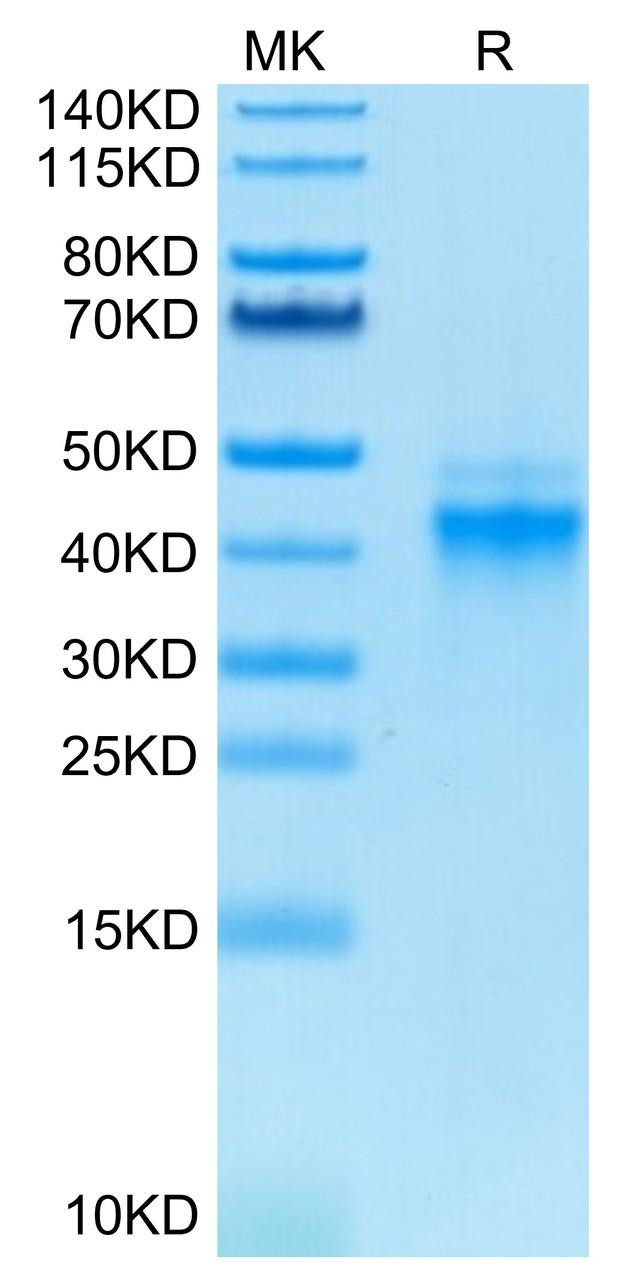
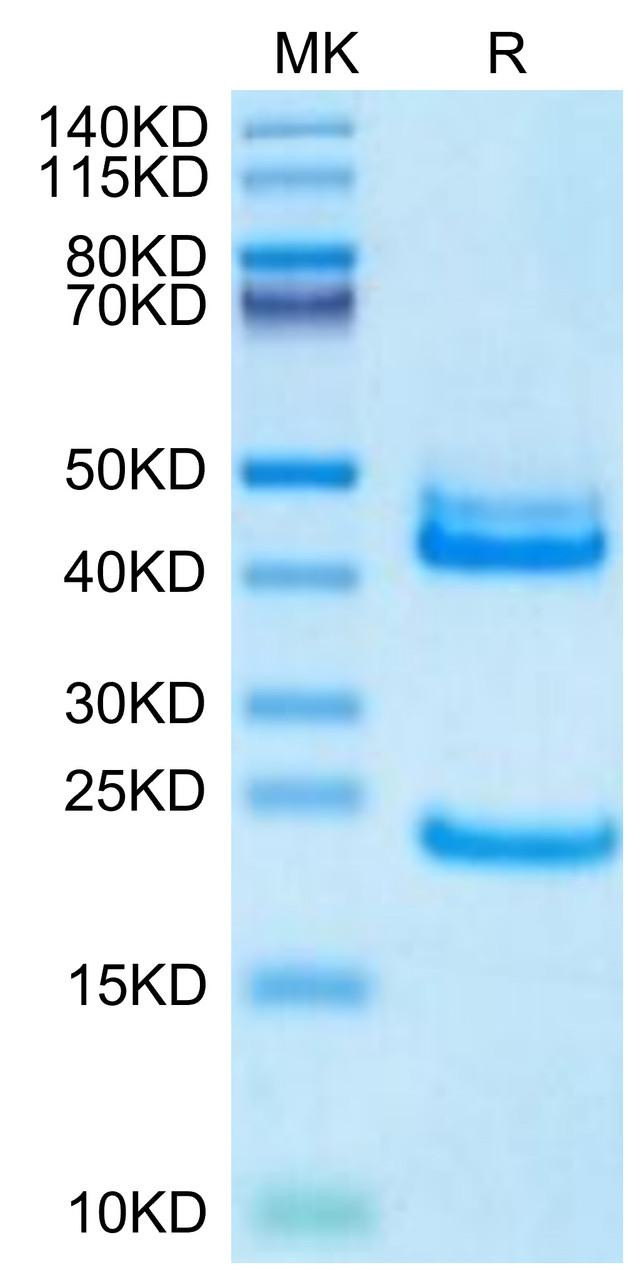
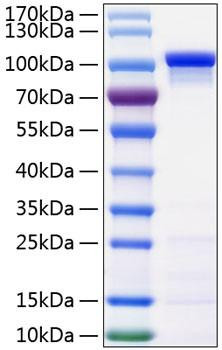
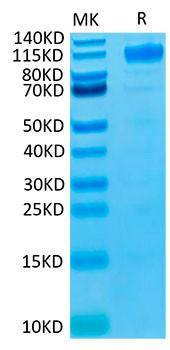
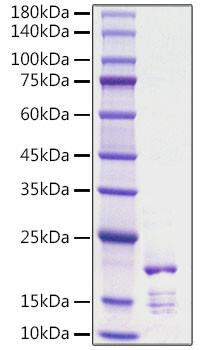
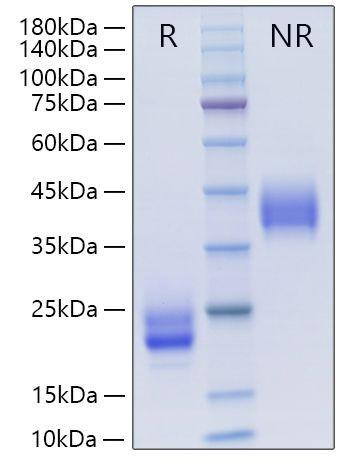
Figure 1: A) Recombinant Human Mature TGF-beta 1 protein IL-4-dependent proliferation of HT‑2 mouse T cells. The ED50 for this effect is 12.85-51.40 pg/mL, corresponding to a specific activity of 1.95×107~7.78×107 units/mg. B) SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis result for a Recombinant Human Mature TGF-beta 1 under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions.
Fast Delivery
7 - 10 Business Day Lead Time
Highly Cited
Thousands of citations across leading scientific journals
PhD Level Support
All our team are trained to a PhD level to support your needs
Our Full Protein Range
Featured Products
Thousands of Citations
Featured in the High-Impact Scientific Journals




Recent Publications
Parasitology and Medicinal Chemistry
Identification and Validation of Compounds Targeting Leishmania major Leucyl-Aminopeptidase M17
Identification and Validation of Compounds Targeting Leishmania major Leucyl-Aminopeptidase M17
Aguado et el.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Minute-sensitive real-time monitoring of neural cells through printed graphene microelectrodes
Minute-sensitive real-time monitoring of neural cells through printed graphene microelectrodes
Niaraki et al.
Frontiers in Microbiology
Osteocytes Serve as a Reservoir for Intracellular Persisting Staphylococcus aureus Due to the Lack of Defense Mechanisms
Osteocytes Serve as a Reservoir for Intracellular Persisting Staphylococcus aureus Due to the Lack of Defense Mechanisms
Garcia-Moreno et al.
Meet Some of the Genie Team!
At Assay Genie, we're here to help every step of the way. Whether you need guidance choosing the right product, updates on your order, or expert support after your purchase, we've got you covered.
Discover our mission to support researchers with cutting-edge solutions.
Find our trusted global partners and explore distribution opportunities.
Get in touch with our team for support, inquiries, or feedback.
Trusted by Researchers, Proven by Results
Frequently asked questions
Customers may place an order in 3 ways. Orders can be made online via pro-forma invoice, on our website, or via email by emailing orders@assaygenie.com. If you wish to send a purchase order, you can find our company under "Assay Genie" or "Reagent Genie Ireland Ltd" on your ordering system. Alternatively, orders may be placed via your local distributor.
Our company can be found under the supplier name "Assay Genie" or "Reagent Genie Ireland Ltd." Still can't find us? Check if we are on your vendor system here. If not, we would be happy to fill out a new supplier form to be registered as a vendor. Alternatively, orders can be placed through your local distributor.
To find out if you can directly order from us or if your order must be made via a distributor click here. Information on your local distributor can be found on this page.
Inquiries can be made online via our 'Contact Us' page. You may also contact us via email at: info@assaygenie.com or orders@assaygenie.com, or by telephone on: +353 15639720. Alternatively, an inquiry can be made via your local distributor.
To create an Assay Genie account, click on 'Register' in the top right corner of the home page. On the registration page fill out the registration details. Once complete, click the 'Create Account' button. To login, click on 'Sign in' in the top right corner of the results page (beside 'Register'). Fill in your email and password and click the 'Sign in' button.
To change the currency of product prices click 'select currency' from the row of options at the top of screen of each web page. Options include: Euro (€), Pound (£), and US Dollar ($).
Once we have received your order a confirmation email will be sent to you. Details such as order number and estimated date of delivery will also be disclosed in this email.