Description
CRYBA4 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (CAB15268)
The CRYBA4 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB15268) is a valuable tool for researchers studying CRYBA4, a protein known to be involved in cataract formation. This antibody is raised in rabbits and has been shown to be highly reactive with human samples, making it ideal for use in various research applications such as Western blotting.CRYBA4 is a crucial protein in the lens of the eye and mutations in this gene have been linked to the development of cataracts. By using this antibody, researchers can better understand the function and regulation of CRYBA4 in the context of eye health and disease.
This antibody enables the detection and analysis of CRYBA4 protein in different cell types, providing valuable insights for studies in ophthalmology and genetics.Overall, the CRYBA4 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB15268) is a reliable tool for researchers looking to explore the role of CRYBA4 in cataract formation and other related eye disorders. Its specificity and sensitivity make it a valuable asset for studies aimed at understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying these conditions.
| Product Name: | CRYBA4 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody |
| SKU: | CAB15268 |
| Size: | 20uL, 100uL |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-196 of human CRYBA4 (NP_001877.1). |
| Sequence: | MTLQ CTKS AGPW KMVV WDED GFQG RRHE FTAE CPSV LELG FETV RSLK VLSG AWVG FEHA GFQG QQYI LERG EYPS WDAW GGNT AYPA ERLT SFRP AACA NHRD SRLT IFEQ ENFL GKKG ELSD DYPS LQAM GWEG NEVG SFHV HSGA WVCS QFPG YRGF QYVL ECDH HSGD YKHF REWG SHAP TFQV QSIR RIQQ |
| Tested Applications: | WB ELISA |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB,1:200 - 1:2000 |
| Synonyms: | CYRBA4; CTRCT23; MCOPCT4; CRYBA4 |
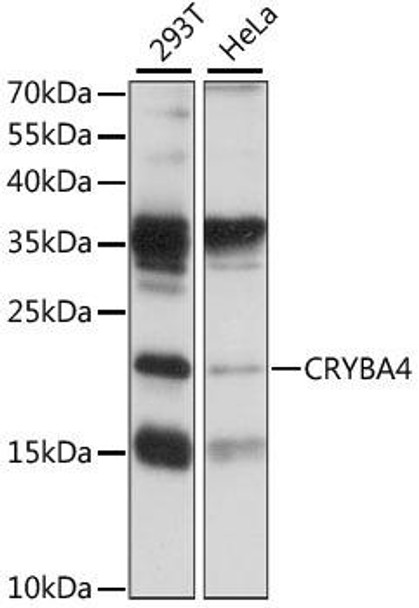
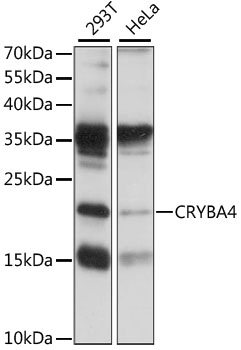
| Positive Sample: | 293T,HeLa |
| Conjugate: | Unconjugated |
| Calculated MW: | 22kDa |
| Observed MW: | 22kDa |
Crystallins are separated into two classes: taxon-specific, or enzyme, and ubiquitous. The latter class constitutes the major proteins of vertebrate eye lens and maintains the transparency and refractive index of the lens. Since lens central fiber cells lose their nuclei during development, these crystallins are made and then retained throughout life, making them extremely stable proteins. Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families; beta and gamma crystallins are also considered as a superfamily. Alpha and beta families are further divided into acidic and basic groups. Seven protein regions exist in crystallins: four homologous motifs, a connecting peptide, and N- and C-terminal extensions. Beta-crystallins, the most heterogeneous, differ by the presence of the C-terminal extension (present in the basic group, none in the acidic group). Beta-crystallins form aggregates of different sizes and are able to self-associate to form dimers or to form heterodimers with other beta-crystallins. This gene, a beta acidic group member, is part of a gene cluster with beta-B1, beta-B2, and beta-B3.
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Gene ID: | 1413 |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.Buffer: PBS with 0.01% thimerosal,50% glycerol,pH7.3. |