COX6B2 Antibody (PACO14281)
- SKU:
- PACO14281
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Applications:
- ELISA
- WB
- IHC
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Conjugation:
- Unconjugated
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | COX6B2 Antibody (PACO14281) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO14281 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, WB, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:2000-1:5000, WB:1:500-1:2000, IHC:1:50-1:200 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Fusion protein of human COX6B2 |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | -20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol |
| Purification Method: | Antigen affinity purification |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
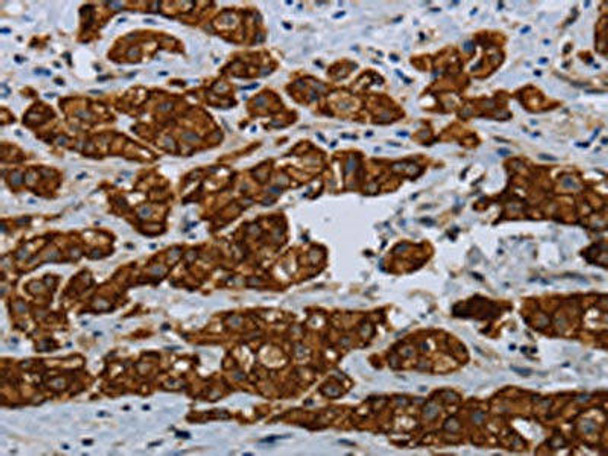
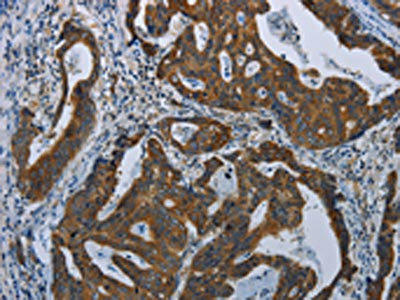 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human gastric cancer tissue using PACO14281(COX6B2 Antibody) at dilution 1/35, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: x200). |
 | Gel: 10%SDS-PAGE, Lysate: 40 μg, Lane: A549 cells, Primary antibody: PACO14281(COX6B2 Antibody) at dilution 1/400, Secondary antibody: Goat anti rabbit IgG at 1/8000 dilution, Exposure time: 5 seconds. |
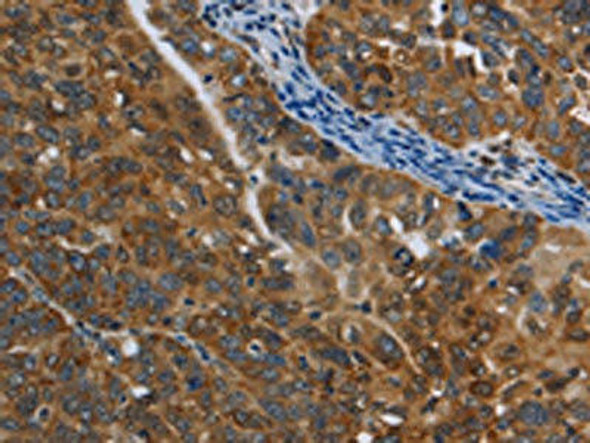
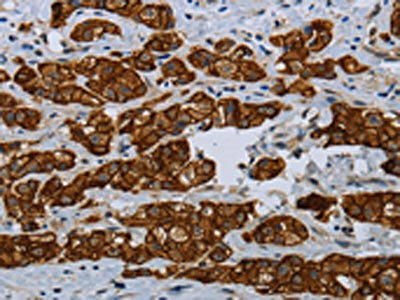 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human breast cancer tissue using PACO14281(COX6B2 Antibody) at dilution 1/35, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: x200). |
| Background: | Cytochrome c oxidase is the terminal enzyme of the electron transfer chain in aerobic bacteria as well as in the mitochondria of plants and animals. Bacterial cytochrome c oxidases are composed of three different subunits and include two hemes a and two copper atoms as prosthetic groups. The enzyme from eukaryotes is more complex and includes three subunits encoded on mitochondrial DNA, which are the homologues of the subunits of the bacterial enzyme, and in addition contains a number of subunits encoded in the nucleus. It is generally agreed that the mitochondrially coded subunits with their associated prosthetic groups are the functional core of the enzyme. The role of the nuclear coded subunits in cytochrome c oxidase function remains a matter of conjecture. cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIb polypeptide 2 Connects the two COX monomers into the physiological dimeric form. |
| Synonyms: | cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIb polypeptide 2 (testis) |
| UniProt Protein Function: | COX6B2: Connects the two COX monomers into the physiological dimeric form. Belongs to the cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Oxidoreductase; Cancer Testis Antigen (CTA); Mitochondrial Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 19q13.42 Cellular Component: mitochondrial crista; mitochondrial intermembrane space Molecular Function:cytochrome-c oxidase activity |
| UniProt Code: | Q6YFQ2 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 74738324 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 125965 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q6YFQ2.1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q6YFQ2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 11kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | COX6B2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CT59; COXVIB2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cancer/testis antigen 59; CT59; Cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIb isoform 2; COX VIb-2; Cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIb, testis-specific isoform |
| Protein Family: | Cytochrome c oxidase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | COX6B2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CX6B2_HUMAN |
| Antibodies |
| COX6B2 Antibody (PACO08551) |
| Secondary Antibody |
| Anti-HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Antibody (CABS014) |
| Recommended Products |
| Anti-FITC Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Antibody (CABS011) |
| Anti-HRP-conjugated Beta Actin Antibody (CABC028) |