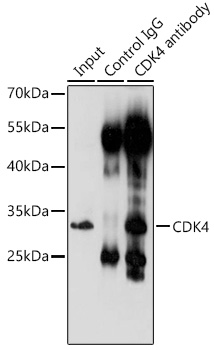
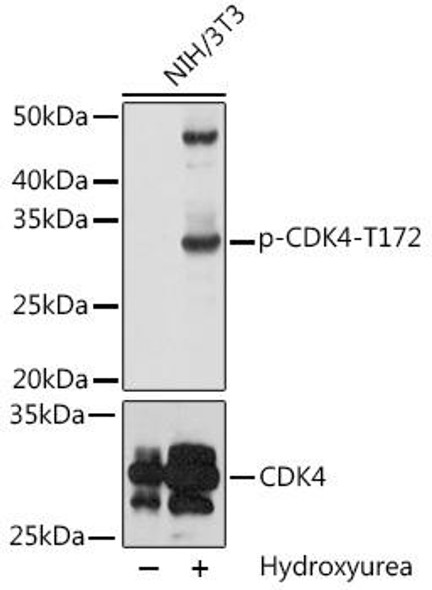
Description
Anti-CDK4 Antibody (CAB0366)
The CDK4 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB0366) is a valuable tool for researchers studying the cell cycle and cell proliferation, with a specific focus on the cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) protein. This antibody, produced in rabbits, is highly specific and reacts strongly with human samples, making it ideal for use in Western blot applications.CDK4 is a key regulator of the cell cycle, promoting cell division and proliferation. Dysregulation of CDK4 activity has been linked to cancer development and progression, making it a promising target for cancer research.
The CDK4 Polyclonal Antibody binds specifically to CDK4, allowing for precise detection and analysis of its expression in a variety of cell types.By understanding the role of CDK4 in cell cycle regulation, researchers can gain insights into the mechanisms underlying cancer growth and potentially identify new therapeutic targets for cancer treatment. The CDK4 Polyclonal Antibody is a valuable tool for advancing our understanding of CDK4 function and its implications in cancer biology.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-CDK4 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB0366 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
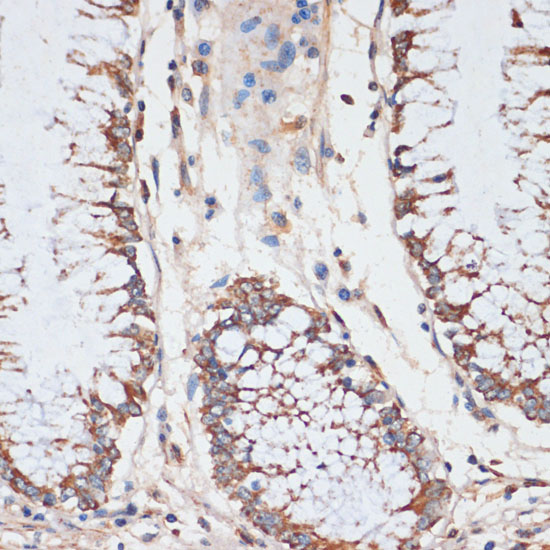
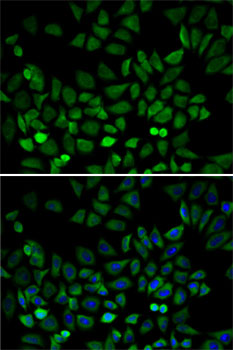
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-303 of human CDK4 (NP_000066.1). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 IP 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
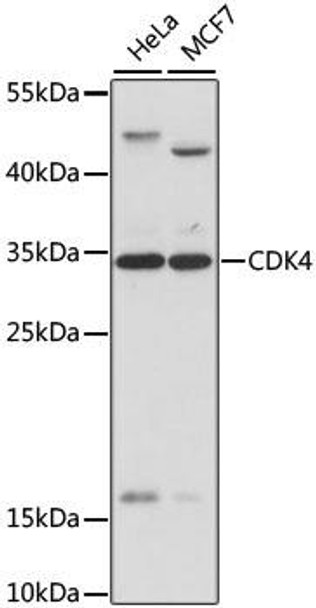
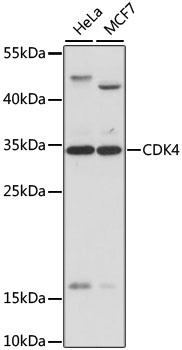
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, MCF7 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-303 of human CDK4 (NP_000066.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MATS RYEP VAEI GVGA YGTV YKAR DPHS GHFV ALKS VRVP NGGG GGGG LPIS TVRE VALL RRLE AFEH PNVV RLMD VCAT SRTD REIK VTLV FEHV DQDL RTYL DKAP PPGL PAET IKDL MRQF LRGL DFLH ANCI VHRD LKPE NILV TSGG TVKL ADFG LARI YSYQ MALT PVVV TLWY RAPE VLLQ STYA TPVD MWSV GCIF AEMF RRKP LFCG NSEA DQLG KIFD LIGL PPED DWPR DVSL PRGA FPPR GPRP VQSV VPEM EESG AQLL LEML TFNP HKRI SAFR ALQH SYLH KDEG NPE |
| Gene ID: | 1019 |
| Uniprot: | P11802 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Membrane, Nucleus |
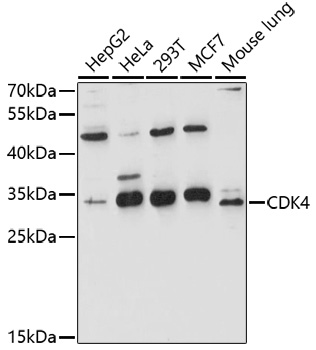
| Calculated MW: | 20kDa/33kDa |
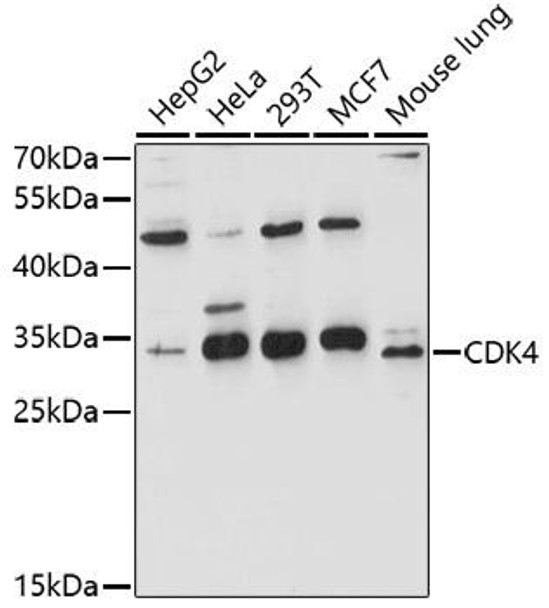
| Observed MW: | 34kDa |
| Synonyms: | CDK4, CMM3, PSK-J3 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28 and S. pombe cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression. The activity of this kinase is restricted to the G1-S phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits D-type cyclins and CDK inhibitor p16(INK4a). This kinase was shown to be responsible for the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product (Rb). Mutations in this gene as well as in its related proteins including D-type cyclins, p16(INK4a) and Rb were all found to be associated with tumorigenesis of a variety of cancers. Multiple polyadenylation sites of this gene have been reported. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CDK4: a protein kinase of the CDK family that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression. Its activity is restricted to the G1-S phase. Controlled by the regulatory subunits D-type cyclins and CDK inhibitor p16(INK4a). Phosphorylates the retinoblastoma gene product (Rb). Point mutations found in somatic and familial melanoma. Amplified in sarcomas, glioma and lymphoma. Amplified, methylated or deleted in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Overexpression drives epithelial tumors in mice. Disruption makes mice resistant to cancer. Inhibitor: PD332991. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 2.7.11.22; Kinase, protein; Protein kinase, CMGC; Cell cycle regulation; Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); CMGC group; CDK family; CDK4 subfamily; CDK/CDK4 subfamily Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 12q14 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; transcription factor complex; nuclear membrane; tight junction; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; nucleolus; cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex; nucleus; chromatin; cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding; cyclin binding; cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity; protein complex binding; cyclin-dependent protein kinase regulator activity; ATP binding Biological Process: circadian rhythm; lens development in camera-type eye; response to drug; establishment and/or maintenance of chromatin architecture; organ regeneration; positive regulation of cell size; positive regulation of translation; positive regulation of apoptosis; response to toxin; response to testosterone stimulus; signal transduction; protein amino acid phosphorylation; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation; response to hyperoxia; regulation of gene expression; cell division; response to lead ion; positive regulation of cell proliferation; mitotic cell cycle; regulation of protein kinase activity; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle Disease: Melanoma, Cutaneous Malignant, Susceptibility To, 3 |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28 and S. pombe cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression. The activity of this kinase is restricted to the G1-S phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits D-type cyclins and CDK inhibitor p16(INK4a). This kinase was shown to be responsible for the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product (Rb). Mutations in this gene as well as in its related proteins including D-type cyclins, p16(INK4a) and Rb were all found to be associated with tumorigenesis of a variety of cancers. Multiple polyadenylation sites of this gene have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P11802 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1168867 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1019 |
| NCBI Accession: | P11802.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P11802,O00576, Q6FG61, B2R9A0, B4DNF9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P11802 |
| Molecular Weight: | Calculated MW: 20kDa/33kDaObserved MW: 34kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | cyclin-dependent kinase 4 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CDK4 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CMM3; PSK-J3 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cyclin-dependent kinase 4; cell division protein kinase 4 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cell division protein kinase 4; PSK-J3 |
| Protein Family: | Cyclin-dependent kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CDK4 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CDK4_HUMAN |