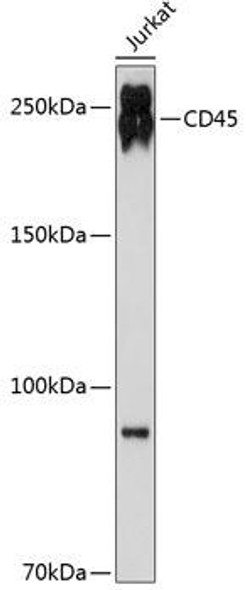
Description
| Product Name: | CD45 monoclonal antibody (APC) |
| Product Code: | AGIM0474 |
| Size: | 100 µL |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Clone: | HI30 |
| Applications: | Flow Cytometry |
| Conjugate: | APC |
| Isotype: | IgG1 |
| Host Species: | Mouse |
| Storage: | Store at 4°C. Avoid prolonged exposure to light. |
| Uniprot: | P08575 |
| Background: | CD45 (LCA, leukocyte common antigen) is a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase ubiquitously expressed in all nucleated hematopoietic cells, comprising approximately 10% of all surface proteins in lymphocytes. CD45 glycoprotein is crucial in lymphocyte development and antigen signaling, serving as an important regulator of Src-family kinases. CD45 protein exists as multiple isoforms as a result of alternative splicing; these isoforms differ in their extracellular domains, whereas they share identical transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. These isoforms differ in their ability to translocate into the glycosphingolipid-enriched membrane domains and their expression depends on cell type and physiological state of the cell. Besides the role in immunoreceptor signaling, CD45 is important in promoting cell survival by modulating integrin-mediated signal transduction pathway and is also involved in DNA fragmentation during apoptosis. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CD45: a receptor type protein tyrosine phosphatase protein. Contains an extracellular domain, a single transmembrane segment and two tandem intracytoplasmic catalytic domains. The first PTPAse domain has enzymatic activity, while the second one seems to affect the substrate specificity of the first one. Specifically expressed in hematopoietic cells. An essential regulator of T- and B-cell antigen receptor signaling. Functions through either direct interaction with components of the antigen receptor complexes, or by activating various Src family kinases required for the antigen receptor signaling. Suppresses JAK kinases, and thus functions as a regulator of cytokine receptor signaling. Four alternatively spliced isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Receptor protein phosphatase, tyrosine; EC 3.1.3.48; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1q31-q32 Cellular Component: focal adhesion; membrane; integral to plasma membrane; plasma membrane; lipid raft; external side of plasma membrane Molecular Function:protein binding; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity; protein kinase binding Biological Process: B cell proliferation; axon guidance; substrate-bound cell migration, cell release from substrate; regulation of cell cycle; protein amino acid dephosphorylation; positive regulation of antigen receptor-mediated signaling pathway; T cell receptor signaling pathway; bone marrow development; B cell receptor signaling pathway; stem cell development; cell surface receptor linked signal transduction; dephosphorylation; positive regulation of protein kinase activity; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol; negative regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity; positive regulation of B cell proliferation; negative regulation of protein kinase activity; hemopoietic progenitor cell differentiation; negative regulation of cytokine and chemokine mediated signaling pathway; positive regulation of T cell proliferation; immunoglobulin biosynthetic process; defense response to virus; T cell differentiation Disease: Hepatitis C Virus, Susceptibility To; Severe Combined Immunodeficiency, Autosomal Recessive, T Cell-negative, B Cell-positive, Nk Cell-positive |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitosis, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP contains an extracellular domain, a single transmembrane segment and two tandem intracytoplasmic catalytic domains, and thus is classified as a receptor type PTP. This PTP has been shown to be an essential regulator of T- and B-cell antigen receptor signaling. It functions through either direct interaction with components of the antigen receptor complexes, or by activating various Src family kinases required for the antigen receptor signaling. This PTP also suppresses JAK kinases, and thus functions as a regulator of cytokine receptor signaling. Alternatively spliced transcripts variants of this gene, which encode distinct isoforms, have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2012] |
| UniProt Code: | P08575 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 44242008 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5788 |
| NCBI Accession: | AAS46946.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P08575,Q16614, Q9H0Y6, A8K7W6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P08575 |
| Molecular Weight: | 61.6kD (predicted) |
| NCBI Full Name: | CD45 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, C |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PTPRC |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | LCA; LY5; B220; CD45; L-CA; T200; CD45R; GP180 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase C; CD45 antigen; T200 glycoprotein; T200 leukocyte common antigen; protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, c polypeptide |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase C |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Leukocyte common antigen; L-CA; T200 |
| Protein Family: | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PTPRC |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PTPRC_HUMAN |