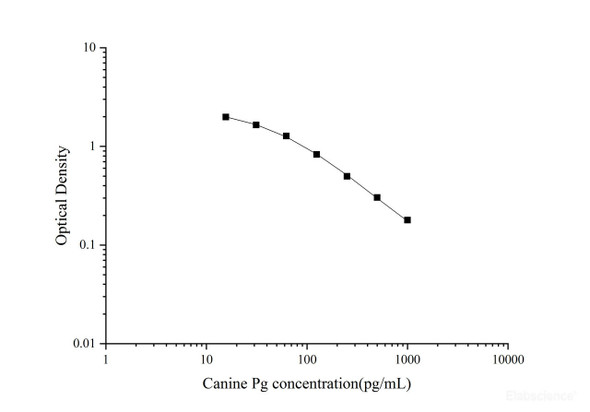
Description
Canine Progesterone (P4) ELISA Kit
Key Features
| Save Time | Pre-coated 96 well plate | |
| Quick Start | Kit includes all necessary reagents | |
| Publication Ready | Reproducible and reliable results |
Overview
| Product Name: | Canine Progesterone (P4) ELISA Kit |
| Product Code: | CNEB0395 |
| Alias: | Progesterone, P4 |
| Reactivity: | General |
| Range: | 0.156-10 ng/mL |
| Detection Method: | Competitive |
| Size: | 96 Assays |
| Storage: | Please see kit components below for exact storage details |
| Note: | For Research Use Only |
Kit Components
| Component | Quantity | Storage |
| ELISA Microplate (Dismountable) | 8x12 strips | -20°C |
| Lyophilized Standard | 2 | -20°C |
| Sample Diluent | 20ml | -20°C |
| Assay Diluent A | 10mL | -20°C |
| Assay Diluent B | 10ml | -20°C |
| Detection Reagent A | 60µL | -20°C |
| Detection Reagent B | 120µL | -20°C |
| Wash Buffer (25X) | 30ml | 4°C |
| Substrate | 10mL | 4°C |
| Stop Solution | 10ml | 4°C |
| Plate Sealer | 5 | - |
Other materials required:
- Microplate reader with 450 nm wavelength filter
- Multichannel Pipette, Pipette, microcentrifuge tubes and disposable pipette tips
- Incubator
- Deionized or distilled water
- Absorbent paper
- Buffer resevoir
Protocol
*Note: Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the correct instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
| Step | Procedure |
| 1. | Add 50µL of Standard, Blank, or Sample per well. The blank well is added with Sample diluent. Solutions are added to the bottom of micro ELISA plate well, avoid inside wall touching and foaming as possible. |
| 2. | Immediately add 50µL of Detection Reagent A working solution to each well. Cover with the Plate sealer. Gently tap the plate to ensure thorough mixing. Incubate for 1 hour at 37°C. Note: if Detection Reagent A appears cloudy warm to room temperature until solution is uniform. |
| 3. | Aspirate each well and wash, repeating the process three times. Wash by filling each well with Wash Buffer (approximately 400µL) (a squirt bottle, multi-channel pipette, manifold dispenser or automated washer are needed) and let it sit in the well for 1-2 minutes. Complete removal of liquid at each step is essential. After the last wash, completely remove remaining Wash Buffer by aspirating or decanting. Invert the plate and pat it against thick clean absorbent paper. |
| 4. | Add 100µL of Detection Reagent B working solution to each well. Cover with the Plate sealer. Incubate for 45 minutes at 37°C. |
| 5. | Repeat the wash process for five times as conducted in step 3. |
| 6. | Add 90µL of Substrate Solution to each well. Cover with a new Plate sealer and incubate for 10-20 minutes at 37°C. Protect the plate from light. The reaction time can be shortened or extended according to the actual color change, but this should not exceed more than 30 minutes. When apparent gradient appears in standard wells, user should terminate the reaction. |
| 7. | Add 50µL of Stop Solution to each well. If color change does not appear uniform, gently tap the plate to ensure thorough mixing. |
| 8. | Determine the optical density (OD value) of each well at once, using amicro-plate reader set to 450 nm. User should open the micro-plate reader in advance, preheat the instrument, and set the testing parameters. |
| 9. | After experiment, store all reagents according to the specified storage temperature respectively until their expiry. |
Sample Preparation
When carrying out an ELISA assay it is important to prepare your samples in order to achieve the best possible results. Below we have a list of procedures for the preparation of samples for different sample types.
| Sample Type | Protocol |
| Serum | If using serum separator tubes, allow samples to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Collect the serum fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. If serum separator tubes are not being used, allow samples to clot overnight at 2-8°C. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Remove serum and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Plasma | Collect plasma using EDTA or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge samples at 4°C for 15 mins at 1000 × g within 30 mins of collection. Collect the plasma fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Note: Over haemolysed samples are not suitable for use with this kit. |
| Urine & Cerebrospinal Fluid | Collect the urine (mid-stream) in a sterile container, centrifuge for 20 mins at 2000-3000 rpm. Remove supernatant and assay immediately. If any precipitation is detected, repeat the centrifugation step. A similar protocol can be used for cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Cell culture supernatant | Collect the cell culture media by pipette, followed by centrifugation at 4°C for 20 mins at 1500 rpm. Collect the clear supernatant and assay immediately. |
| Cell lysates | Solubilize cells in lysis buffer and allow to sit on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge tubes at 14,000 x g for 5 minutes to remove insoluble material. Aliquot the supernatant into a new tube and discard the remaining whole cell extract. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Tissue homogenates | The preparation of tissue homogenates will vary depending upon tissue type. Rinse tissue with 1X PBS to remove excess blood & homogenize in 20ml of 1X PBS (including protease inhibitors) and store overnight at ≤ -20°C. Two freeze-thaw cycles are required to break the cell membranes. To further disrupt the cell membranes you can sonicate the samples. Centrifuge homogenates for 5 mins at 5000xg. Remove the supernatant and assay immediately or aliquot and store at -20°C or -80°C. |
| Tissue lysates | Rinse tissue with PBS, cut into 1-2 mm pieces, and homogenize with a tissue homogenizer in PBS. Add an equal volume of RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors and lyse tissues at room temperature for 30 minutes with gentle agitation. Centrifuge to remove debris. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C |
| Breast Milk | Collect milk samples and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 60 min at 4°C. Aliquot the supernatant and assay. For long term use, store samples at -80°C. Minimize freeze/thaw cycles. |
Canine P4 Background
Progesterone (P4) is a naturally occurring hormone primarily produced by the ovaries after ovulation during the second half of the menstrual cycle. It plays a crucial role in the female reproductive system. Progesterone prepares the uterus for pregnancy by thickening the uterine lining (endometrium) to provide a suitable environment for the implantation of a fertilized egg. If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone levels drop, leading to the shedding of the uterine lining and the start of menstruation.
Functions of Progesterone
Progesterone serves various functions, including preparing the uterine lining for implantation, maintaining the uterine lining during pregnancy, suppressing ovulation, preventing multiple pregnancies, relaxing the uterus to prevent premature labor, supporting bone health, regulating metabolism, and aiding in breast development and milk production during lactation.
Hormone Imbalance and Progesterone Therapy
Imbalances in progesterone levels can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, difficulties in conceiving, an increased risk of miscarriage, and symptoms such as mood swings, fatigue, and breast tenderness. Progesterone therapy, using synthetic progestins or natural progesterone, can help address these imbalances, regulate the menstrual cycle, support fertility treatments, alleviate menopausal symptoms, or prevent preterm labor. However, it should always be administered under medical supervision due to potential side effects and interactions with other medications. Individual hormone levels and specific medical conditions should be considered for appropriate dosage and duration of therapy.
Canine P4 FAQs
What is the Canine P4 ELISA Kit?
The Canine P4 ELISA Kit is a diagnostic tool used to measure progesterone levels in biological samples. It provides a simple and efficient method for quantitative detection of Canine P4 levels.
How does the Canine P4 ELISA Kit work?
The Canine P4 ELISA Kit uses an ELISA to detect and measure Progesterone (P4) levels in biological samples. It captures P4 molecules using specially coated microplate wells, and a colorimetric reaction is triggered with the addition of P4 antibodies and enzyme-conjugated secondary antibodies. The resulting color intensity corresponds to P4 concentration.
What are the advantages of using the Canine P4 ELISA Kit?
The Canine P4 ELISA Kit offers several advantages. It provides accurate and reliable quantitative results, enabling precise progesterone level determination. The kit is specifically designed for canine samples, ensuring optimal sensitivity and specificity.
Are there any specific storage or handling requirements for the Canine P4 ELISA Kit?
It is important to store the kit components according to the instructions provided. Typically, the kit should be stored at the recommended temperature, protected from light and moisture. Additionally, proper handling techniques, including following good laboratory practices, should be followed to ensure optimal performance.
Where can I find more information about the Canine P4 ELISA Kit?
For more detailed information about the Canine P4 ELISA Kit, including technical specifications, performance characteristics, and ordering details, please refer to the product brochure or contact our customer support team. We are here to assist you with any inquiries you may have.