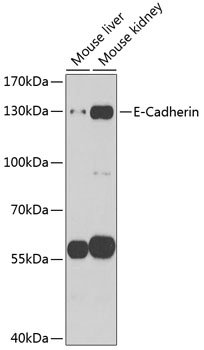
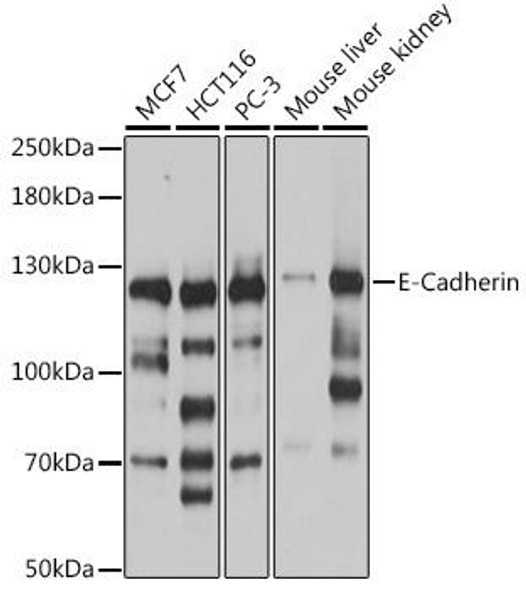
Description
Anti-E-Cadherin Antibody (CAB11509)
The Cadherin-1 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB11509) is a valuable tool for researchers studying Cadherin-1, a cell adhesion molecule essential for maintaining tissue integrity and cell communication. This antibody, produced in rabbits, exhibits high reactivity with human samples and has been validated for use in Western blot applications. By specifically binding to Cadherin-1, researchers can accurately detect and analyze this protein in various cell types, making it suitable for studies in developmental biology, tissue morphogenesis, and cancer research.Cadherin-1, also known as E-cadherin, plays a crucial role in cell adhesion and signaling pathways that regulate cell behavior and tissue organization. Dysregulation of Cadherin-1 expression is associated with various diseases, including cancer metastasis and developmental disorders.
Therefore, research focusing on Cadherin-1 can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying these conditions and facilitate the development of targeted therapies.With its ability to accurately detect and analyze Cadherin-1 in biological samples, the Cadherin-1 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB11509) is an essential tool for researchers investigating the role of Cadherin-1 in health and disease. Its versatility and specificity make it an invaluable asset in advancing our understanding of cell adhesion biology and potentially identifying new therapeutic targets for disease intervention.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-E-Cadherin Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB11509 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 700-800 of human E-Cadherin (NP_004351.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:1000 |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | Mouse liver, Mouse kidney |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 700-800 of human E-Cadherin (NP_004351.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | PVEA GLQI PAIL GILG GILA LLIL ILLL LLFL RRRA VVKE PLLP PEDD TRDN VYYY DEEG GGEE DQDF DLSQ LHRG LDAR PEVT RNDV APTL MSVP RYLP R |
| Gene ID: | 999 |
| Uniprot: | P12830 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell junction, Cell membrane, Endosome, Golgi apparatus, Single-pass type I membrane protein, trans-Golgi network |
| Calculated MW: | 90kDa/97kDa |
| Observed MW: | 130kDa |
| Synonyms: | Arc-1, CD324, CDHE, ECAD, LCAM, UVO, CDH1, E-Cadherin |
| Background: | This gene encodes a classical cadherin of the cadherin superfamily. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate the mature glycoprotein. This calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion protein is comprised of five extracellular cadherin repeats, a transmembrane region and a highly conserved cytoplasmic tail. Mutations in this gene are correlated with gastric, breast, colorectal, thyroid and ovarian cancer. Loss of function of this gene is thought to contribute to cancer progression by increasing proliferation, invasion, and/or metastasis. The ectodomain of this protein mediates bacterial adhesion to mammalian cells and the cytoplasmic domain is required for internalization. This gene is present in a gene cluster with other members of the cadherin family on chromosome 16. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Function: Cadherins are calcium-dependent cell adhesion proteins. They preferentially interact with themselves in a homophilic manner in connecting cells; cadherins may thus contribute to the sorting of heterogeneous cell types. CDH1 is involved in mechanisms regulating cell-cell adhesions, mobility and proliferation of epithelial cells. Has a potent invasive suppressor role. It is a ligand for integrin alpha-E/beta-7. Ref.22E-Cad/CTF2 promotes non-amyloidogenic degradation of Abeta precursors. Has a strong inhibitory effect on APP C99 and C83 production. Ref.22 |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Subunit structure: Homodimer; disulfide-linked. Component of an E-cadherin/ catenin adhesion complex composed of at least E-cadherin/CDH1, beta-catenin/CTNNB1 or gamma-catenin/JUP, and potentially alpha-catenin/CTNNA1; the complex is located to adherens junctions. The stable association of CTNNA1 is controversial as CTNNA1 was shown not to bind to F-actin when assembled in the complex. Alternatively, the CTNNA1-containing complex may be linked to F-actin by other proteins such as LIMA1. Interaction with PSEN1, cleaves CDH1 resulting in the disassociation of cadherin-based adherens junctions (CAJs). Interacts with AJAP1, CTNND1 and DLGAP5 By similarity. Interacts with TBC1D2. Interacts with LIMA1. Interacts with CAV1. Interacts with the TRPV4 and CTNNB1 complex By similarity. Ref.16 Ref.17 Ref.18 Ref.19 Ref.20 Ref.25 Ref.26 Subcellular location: Cell junction. Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Endosome. Golgi apparatus trans-Golgi network. Note: Colocalizes with DLGAP5 at sites of cell-cell contact in intestinal epithelial cells. Anchored to actin microfilaments through association with alpha-, beta- and gamma-catenin. Sequential proteolysis induced by apoptosis or calcium influx, results in translocation from sites of cell-cell contact to the cytoplasm. Colocalizes with RAB11A endosomes during its transport from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane. Ref.4 Ref.18 Ref.21 Tissue specificity: Non-neural epithelial tissues. Induction: Expression is repressed by MACROD1. Ref.23 Post-translational modification: During apoptosis or with calcium influx, cleaved by a membrane-bound metalloproteinase (ADAM10), PS1/gamma-secretase and caspase-3 to produce fragments of about 38 kDa (E-CAD/CTF1), 33 kDa (E-CAD/CTF2) and 29 kDa (E-CAD/CTF3), respectively. Processing by the metalloproteinase, induced by calcium influx, causes disruption of cell-cell adhesion and the subsequent release of beta-catenin into the cytoplasm. The residual membrane-tethered cleavage product is rapidly degraded via an intracellular proteolytic pathway. Cleavage by caspase-3 releases the cytoplasmic tail resulting in disintegration of the actin microfilament system. The gamma-secretase-mediated cleavage promotes disassembly of adherens junctions. Ref.4 Ref.12 Ref.15N-glycosylation at Asn-637 is essential for expression, folding and trafficking. Involvement in Disease: Defects in CDH1 are the cause of hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (HDGC) [ MIM:137215]. An autosomal dominant cancer predisposition syndrome with increased susceptibility to diffuse gastric cancer. Diffuse gastric cancer is a malignant disease characterized by poorly differentiated infiltrating lesions resulting in thickening of the stomach. Malignant tumors start in the stomach, can spread to the esophagus or the small intestine, and can extend through the stomach wall to nearby lymph nodes and organs. It also can metastasize to other parts of the body. Note=Heterozygous germline mutations CDH1 are responsible for familial cases of diffuse gastric cancer. Somatic mutations in the has also been found in patients with sporadic diffuse gastric cancer and lobular breast cancer. Ref.36 Ref.41Defects in CDH1 are a cause of susceptibility to endometrial cancer (ENDMC) [ MIM:608089].Defects in CDH1 are a cause of susceptibility to ovarian cancer (OC) [ MIM:167000]. Ovarian cancer common malignancy originating from ovarian tissue. Although many histologic types of ovarian neoplasms have been described, epithelial ovarian carcinoma is the most common form. Ovarian cancers are often asymptomatic and the recognized signs and symptoms, even of late-stage disease, are vague. Consequently, most patients are diagnosed with advanced disease. Sequence similarities: Contains 5 cadherin domains. Sequence caution: The sequence AAA61259.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Frameshift at positions 16, 22, 25, 28, 31, 34, 52, 67, 73, 76, 94, 102, 633 and 636. |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is a classical cadherin from the cadherin superfamily. The encoded protein is a calcium dependent cell-cell adhesion glycoprotein comprised of five extracellular cadherin repeats, a transmembrane region and a highly conserved cytoplasmic tail. Mutations in this gene are correlated with gastric, breast, colorectal, thyroid and ovarian cancer. Loss of function is thought to contribute to progression in cancer by increasing proliferation, invasion, and/or metastasis. The ectodomain of this protein mediates bacterial adhesion to mammalian cells and the cytoplasmic domain is required for internalization. Identified transcript variants arise from mutation at consensus splice sites. [provided by RefSeq] |
| UniProt Code: | P12830 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 399166 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 999 |
| NCBI Accession: | P12830.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P12830,Q13799, Q14216, Q15855, Q16194, Q4PJ14, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P12830,Q9UII7,Q9UII8 |
| Molecular Weight: | 97,456 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cadherin-1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | cadherin 1, type 1, E-cadherin (epithelial) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CDH1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | UVO; CDHE; ECAD; LCAM; Arc-1; CD324 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cadherin-1; CAM 120/80; E-Cadherin; uvomorulin; cell-CAM 120/80; OTTHUMP00000174868; epithelial cadherin; cadherin 1, E-cadherin (epithelial); calcium-dependent adhesion protein, epithelial |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cadherin-1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | CAM 120/80; Epithelial cadherin; E-cadherin; Uvomorulin |
| Protein Family: | Cadherin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CDH1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CADH1_HUMAN |