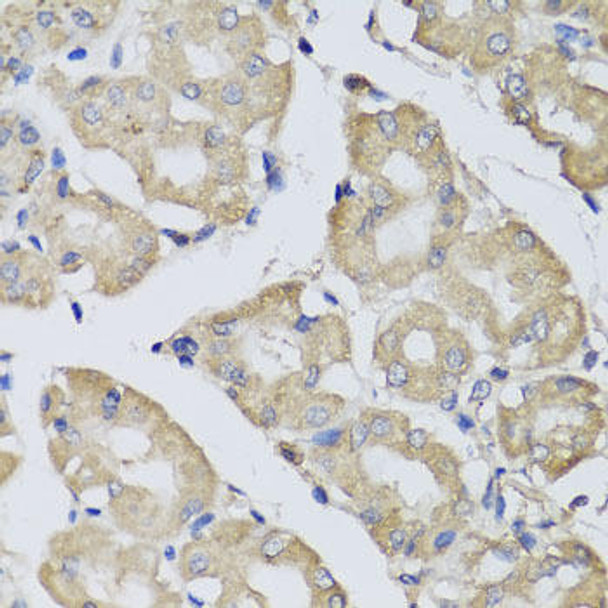
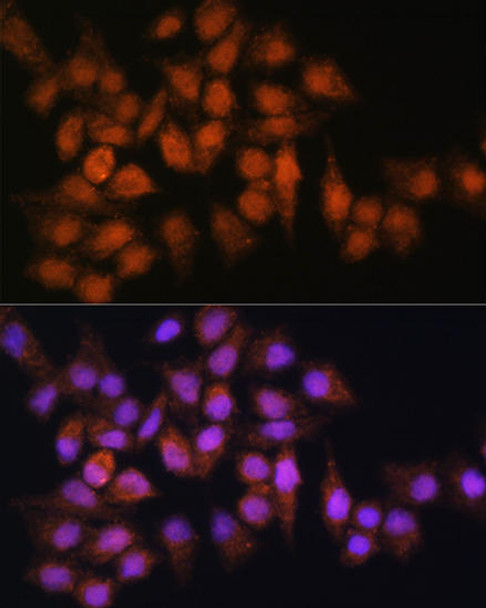
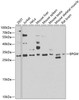
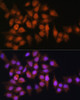
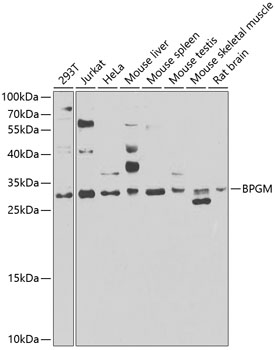
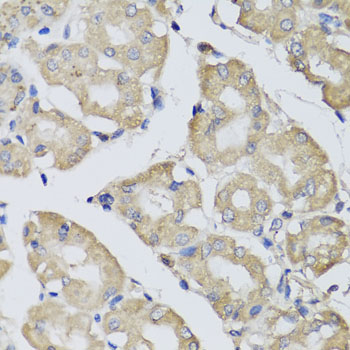
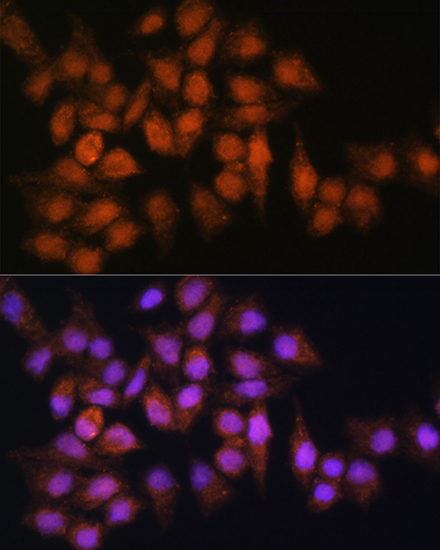
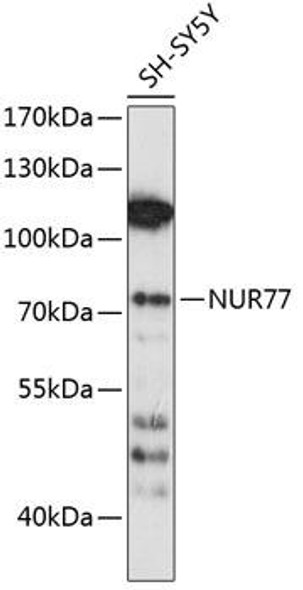
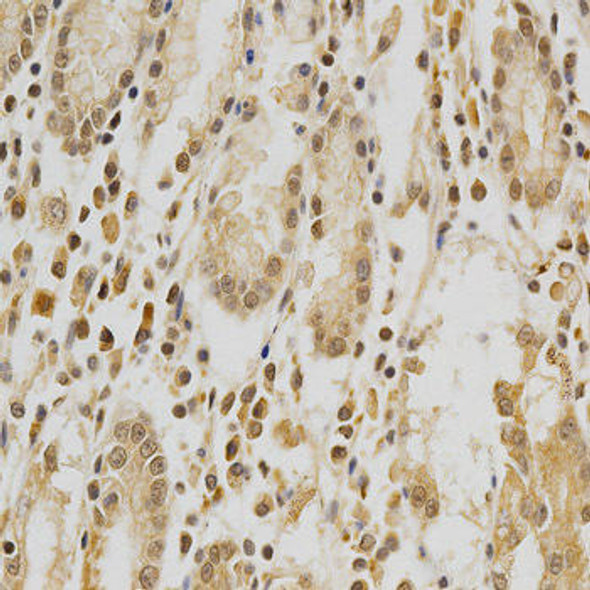
Anti-BPGM Antibody (CAB7880)
- SKU:
- CAB7880
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Metabolism
Description
Anti-BPGM Antibody (CAB7880)
The BPGM Polyclonal Antibody (CAB7880) is a valuable tool for researchers studying BPGM, an enzyme involved in the metabolism of glucose-1-phosphate. This antibody, raised in rabbits, shows high reactivity with human samples and has been validated for use in Western blot applications. By specifically binding to the BPGM protein, researchers can easily detect and analyze its expression in various cell types.BPGM is a key enzyme in the glycolytic pathway, playing a crucial role in energy production and metabolism. Dysregulation of BPGM has been implicated in various metabolic disorders and diseases, making it an important target for further research.
By studying the activity of BPGM, researchers can gain insights into metabolic pathways and potentially develop new therapeutic strategies for metabolic-related conditions.Overall, the BPGM Polyclonal Antibody is a reliable tool for researchers interested in studying the role of BPGM in metabolism and its potential implications in metabolic diseases. Its high reactivity, specificity, and validated applications make it an ideal choice for studies in biochemistry, molecular biology, and metabolic research.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-BPGM Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB7880 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-259 of human BPGM (NP_001715.1). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | 293T, Jurkat, HeLa, Mouse liver, Mouse spleen, Mouse testis, Mouse skeletal muscle, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-259 of human BPGM (NP_001715.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MSKY KLIM LRHG EGAW NKEN RFCS WVDQ KLNS EGME EARN CGKQ LKAL NFEF DLVF TSVL NRSI HTAW LILE ELGQ EWVP VESS WRLN ERHY GALI GLNR EQMA LNHG EEQV RLWR RSYN VTPP PIEE SHPY YQEI YNDR RYKV CDVP LDQL PRSE SLKD VLER LLPY WNER IAPE VLRG KTIL ISAH GNSS RALL KHLE GISD EDII NITL PTGV PILL ELDE NLRA VGPH QFLG DQEA IQAA IKKV EDQG KVKQ AKK |
| Gene ID: | 669 |
| Uniprot: | P07738 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 30kDa |
| Observed MW: | 30kDa |
| Synonyms: | BPGM, DPGM |
| Background: | 2, 3-diphosphoglycerate (2, 3-DPG) is a small molecule found at high concentrations in red blood cells where it binds to and decreases the oxygen affinity of hemoglobin. This gene encodes a multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes 2, 3-DPG synthesis via its synthetase activity, and 2, 3-DPG degradation via its phosphatase activity. The enzyme also has phosphoglycerate phosphomutase activity. Deficiency of this enzyme increases the affinity of cells for oxygen. Mutations in this gene result in hemolytic anemia. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | BPGM: Plays a major role in regulating hemoglobin oxygen affinity by controlling the levels of its allosteric effector 2,3- bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG). Also exhibits mutase (EC 5.4.2.1) and phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.13) activities. Defects in BPGM are the cause of bisphosphoglycerate mutase deficiency (BPGMD). A disease characterized by hemolytic anemia, splenomegaly, cholelithiasis and cholecystitis. Belongs to the phosphoglycerate mutase family. BPG- dependent PGAM subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 5.4.2.4; EC 3.1.3.13; Carbohydrate Metabolism - glycolysis and gluconeogenesis; Phosphatase (non-protein); EC 5.4.2.11; Isomerase Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 7q33 Molecular Function:phosphoglycerate mutase activity; bisphosphoglycerate mutase activity; bisphosphoglycerate phosphatase activity Biological Process: erythrocyte development; glycolysis; dephosphorylation; carbohydrate metabolic process; respiratory gaseous exchange Disease: Bisphosphoglycerate Mutase Deficiency |
| NCBI Summary: | 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG) is a small molecule found at high concentrations in red blood cells where it binds to and decreases the oxygen affinity of hemoglobin. This gene encodes a multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes 2,3-DPG synthesis via its synthetase activity, and 2,3-DPG degradation via its phosphatase activity. The enzyme also has phosphoglycerate phosphomutase activity. Deficiency of this enzyme increases the affinity of cells for oxygen. Mutations in this gene result in hemolytic anemia. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P07738 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 130350 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 669 |
| NCBI Accession: | P07738.2 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P07738 |
| Molecular Weight: | 30kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Bisphosphoglycerate mutase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | bisphosphoglycerate mutase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | BPGM |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | DPGM; ECYT8 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | bisphosphoglycerate mutase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Bisphosphoglycerate mutase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate mutase, erythrocyte; 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate synthase (EC:3.1.3.13, EC:5.4.2.11); 2,3-diphosphoglycerate mutase; DPGM; BPG-dependent PGAM |
| Protein Family: | Bisphosphoglycerate mutase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | BPGM |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PMGE_HUMAN |