Gemtuzumab Biosimilar: Advancing CD33-Targeted Therapy for AML
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin is a CD33-targeting antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) approved for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). By selectively delivering a cytotoxic payload to CD33-positive leukemia cells, Gemtuzumab has revolutionized AML therapy. The biosimilar HDBS0015 offers equivalent efficacy and safety as the original biologic at a lower cost, expanding access to this life-saving treatment.
This article explores the mechanism of action, clinical applications, and benefits of HDBS0015 in AML therapy.
1. Understanding CD33 and Its Role in AML
What is CD33?
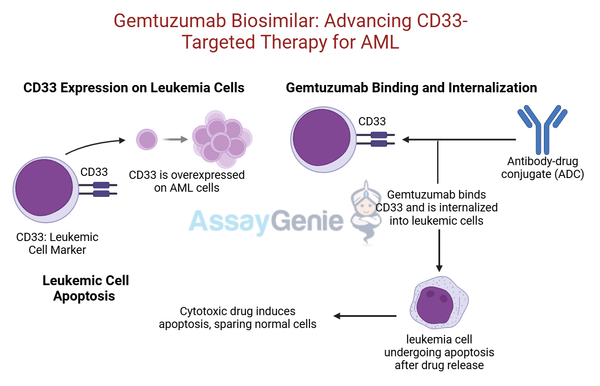
CD33 is a myeloid differentiation antigen expressed on the surface of AML cells but not on normal hematopoietic stem cells. This selective expression makes CD33 an ideal target for ADC-based therapies.
Gemtuzumab: Targeting CD33
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin combines a monoclonal antibody against CD33 with a cytotoxic agent, calicheamicin, to selectively destroy AML cells.
2. HDBS0015: A Cost-Effective Biosimilar
What is HDBS0015?
HDBS0015 is a biosimilar of Gemtuzumab ozogamicin, developed to provide the same clinical efficacy, safety, and quality at a reduced cost.
Key Features of HDBS0015
- Target: CD33-positive AML cells.
- Mechanism: Delivers calicheamicin directly to cancer cells, sparing healthy tissues.
- Affordability: Reduces the financial burden of ADC therapy, making it more accessible worldwide.
3. Mechanism of Action
Step | Details |
|---|---|
CD33 Binding | |
Internalization | The antibody-CD33 complex is internalized into the AML cell. |
Calicheamicin Release | The cytotoxic calicheamicin payload is released inside the cell, targeting DNA. |
Cell Death | Calicheamicin induces double-strand DNA breaks, leading to apoptosis in AML cells. |
4. Clinical Applications
HDBS0015 is indicated for the treatment of newly diagnosed and relapsed or refractory AML in patients with CD33-positive disease.
Newly Diagnosed AML
- Combination Therapy: Used with standard chemotherapy (e.g., daunorubicin and cytarabine) to improve remission rates.
- Monotherapy: Effective in patients who are not candidates for intensive chemotherapy.
Relapsed or Refractory AML
- Targets residual or drug-resistant AML cells, extending survival in heavily pretreated patients.
5. Benefits of HDBS0015
Targeted Tumor Destruction
By delivering calicheamicin directly to CD33-positive cells, HDBS0015 minimizes off-target effects and systemic toxicity.
Cost-Effective Treatment
HDBS0015 offers a more affordable option compared to the reference biologic, increasing accessibility for patients worldwide.
Combination Therapy Potential
HDBS0015 enhances the efficacy of standard AML therapies, providing durable responses and improved survival rates.
6. Challenges and Considerations
Adverse Effects
- Hematologic Toxicity: Includes thrombocytopenia and neutropenia, manageable with supportive care.
- Hepatotoxicity: Rare cases of veno-occlusive disease (VOD) may occur, requiring monitoringand early intervention.
Resistance Development
AML cells may develop resistance to Gemtuzumab by downregulating CD33 expression. Combination therapies can help mitigate this risk.
7. Comparison: Gemtuzumab vs. HDBS0015
Feature | Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin | HDBS0015 (Biosimilar) |
|---|---|---|
Target | CD33-positive AML cells. | CD33-positive AML cells. |
Mechanism | Delivers calicheamicin to induce DNA damage and apoptosis. | Delivers calicheamicin to induce DNA damage and apoptosis. |
Indications | Newly diagnosed and relapsed/refractory AML. | Newly diagnosed and relapsed/refractory AML. |
Efficacy | Proven in clinical trials. | Equivalent in preclinical and clinical studies. |
Cost | High | Reduced, improving accessibility. |
8. Future Directions
Expanded Indications
- Exploring the use of HDBS0015 in minimal residual disease (MRD) settings to prevent relapse.
- Evaluating its potential in pediatric AML where CD33 is overexpressed.
Novel Combinations
- Checkpoint Inhibitors: Combining HDBS0015 with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors may enhance immune-mediated clearance of AML cells.
- Targeted Agents: Synergistic effects with FLT3 inhibitors in FLT3-mutated AML.
9. Summary Table
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Target | |
Primary Use | Treatment of newly diagnosed and relapsed/refractory AML.The antibody-CD33 complex is internalized into the AML cell. |
Mechanism of Action | ADC delivering calicheamicin to induce DNA damage and apoptosis. |
Biosimilar Benefits | Affordable, accessible, and clinically equivalent to Gemtuzumab. |
Conclusion
The Gemtuzumab biosimilar HDBS0015 represents a significant advancement in AML treatment. By targeting CD33, HDBS0015 delivers potent anti-cancer activity while minimizing systemic toxicity. As a cost-effective alternative, HDBS0015 expands access to this life-saving therapy, providing new hope for AML patients globally.
References
- Castaigne, S., et al., 2012. Addition of Gemtuzumab ozogamicin to chemotherapy improves survival in AML. NEJM, 367(5),
pp. 454-460. - Amadori, S., et al., 2016. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in AML: Clinical evidence and future directions. Journal of Clinical
Oncology, 34(10), pp. 1217-1223. - ClinicalTrials.gov, 2023. Trials involving Gemtuzumab ozogamicin and biosimilar HDBS0015. Available at www.clinicaltrials.gov.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA), 2023. Biosimilar guidelines for antibody-drug conjugates in oncology. Available at www.ema.europa.eu.
- Hills, R.K., et al., 2014. Incorporating Gemtuzumab into frontline AML therapy: Evidence and future perspectives. Leukemia,
28(7), pp. 1200-1208.
Recent Posts
-
Tigatuzumab Biosimilar: Harnessing DR5 for Targeted Cancer Therapy
Tigatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting death receptor 5 (DR5), a member of the …17th Dec 2025 -
Enavatuzumab Biosimilar: Advancing TWEAKR-Targeted Therapy in Cancer
Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting TWEAK receptor (TWEAKR, also known as …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab Biosimilar: Advancing CD52-Targeted Therapy
Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD52, a glycoprotein highly expressed o …17th Dec 2025