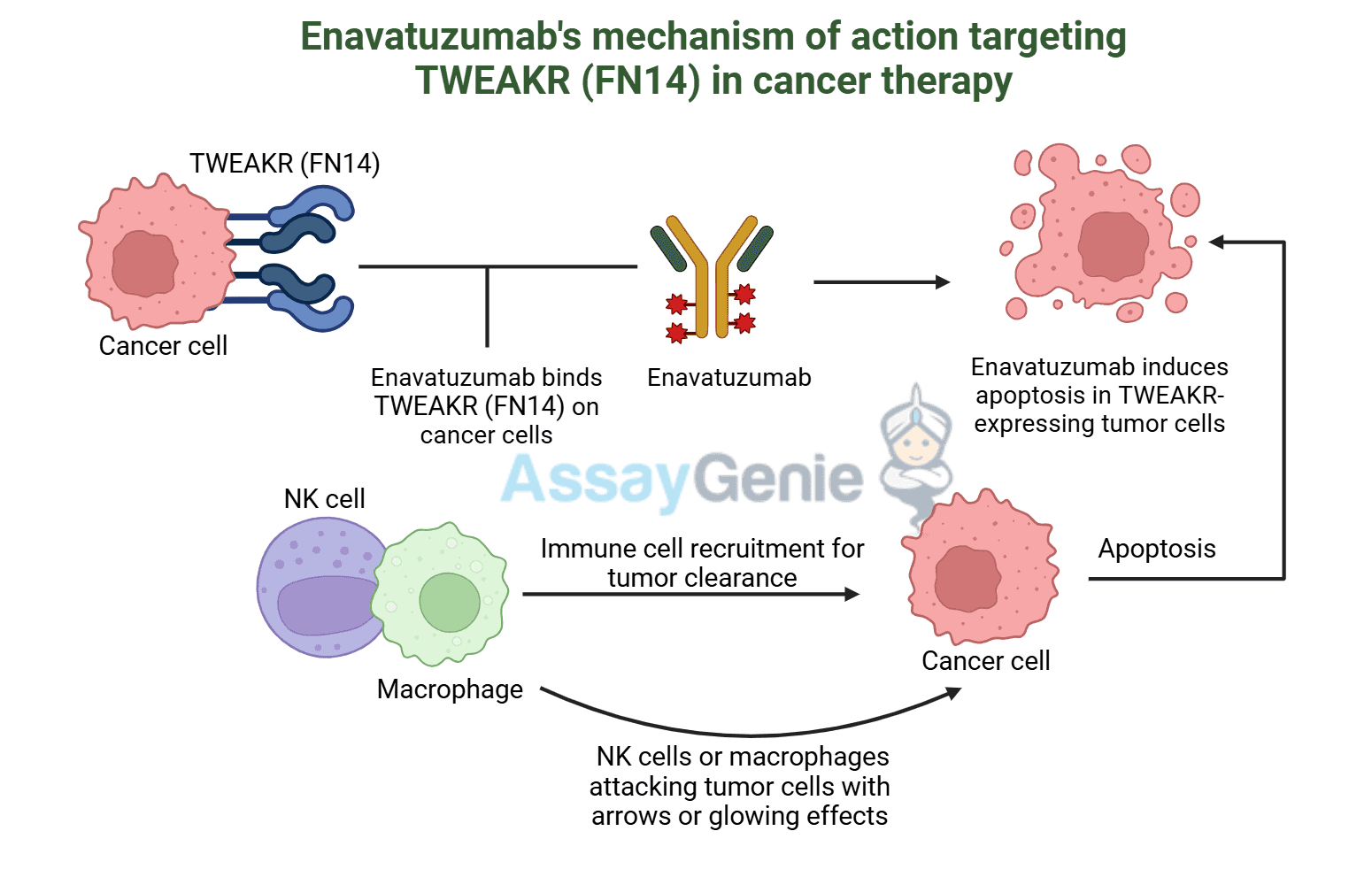
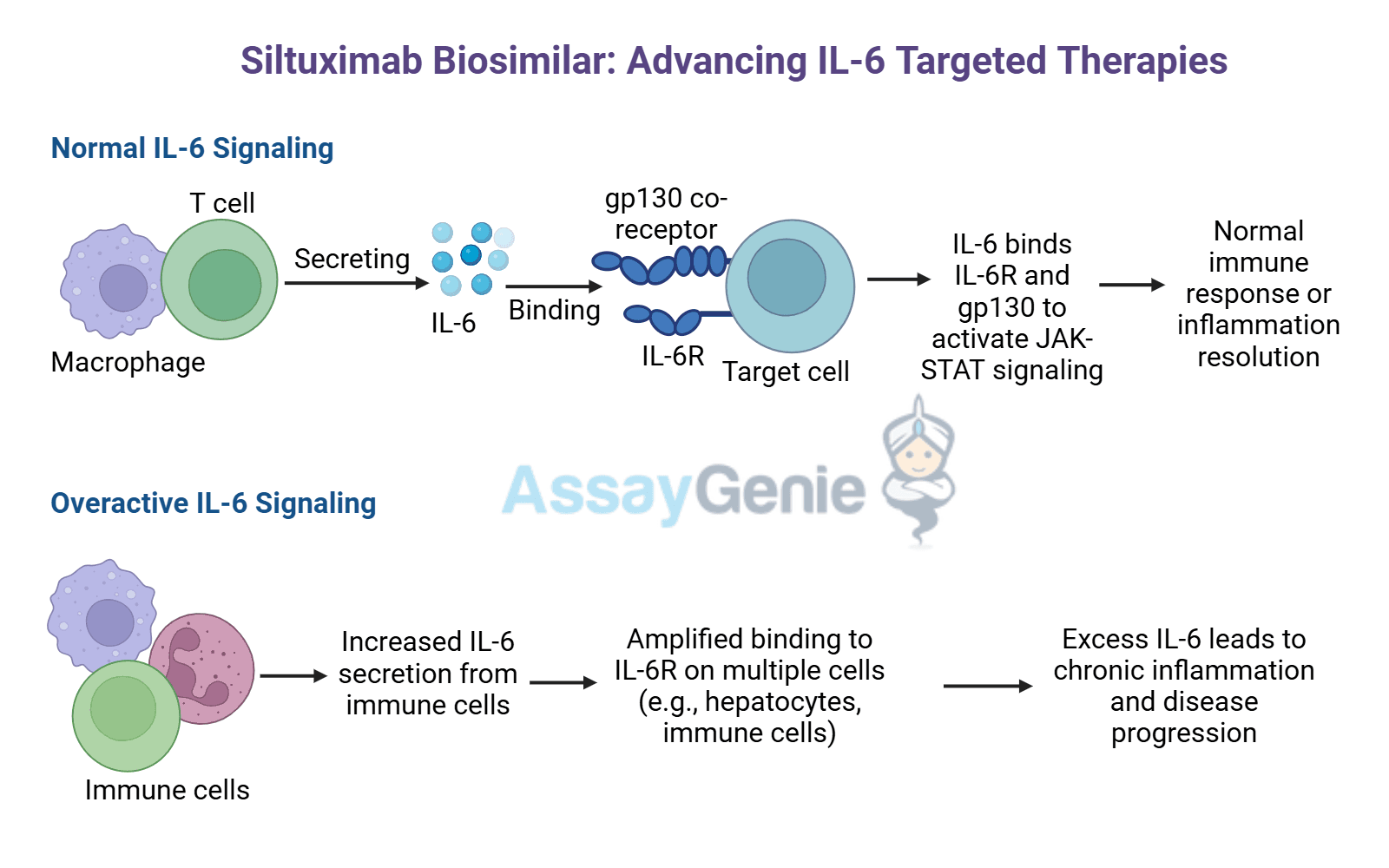
Biosimilar Antibodies
Biosimilar Antibodies
Functional-grade biosimilars for in vitro and in vivo experiments, validated to support innovation in drug discovery, molecular biology, and cell-based assays!

Our Biosimilar Range
Why choose Biosimilar Antibodies?
- Cost-effective and reliable alternatives to reference biologics.
- Validated for diverse applications, including ELISAs, flow cytometry, and Western blotting.
- Suitable for biophysical characterization (SPR) and immunohistochemistry (IHC).
- Proven functionality in blocking, neutralization, co-stimulation, and depletion assays.
Testimonials & Partners
Delivery in 7-10 business days
24 hours on LiveChat & PhD level support
Cost-effective alternative to therapeutic mAbs
Ensuring reproducible results
cGMP & ISO Certification


Quality is at the core of everything we do.
Manufactured in state-of-the-art facilities, our products meet the highest standards, including current Good Manufacturing Practicies) cGMP, ISO 9001:2015, and ISO 13485:2016 certifications. These ensure consistent quality, customer-focused innovation, and reliable performance in every batch.
Biosimilar Production
Assay Genie's Biosimilar Development Pipeline creates research-grade biosimilars. We select and characterize reference biologics, then design and express them in host cells. Precise purification yields high-quality antibodies. Rigorous quality control validates structural integrity and functionality. This process ensures reliable biosimilar solutions for research.
Biosimilar Antibody Product Data
Reference Biosimilars
Our Reference & Conjugated Biosimilars demonstrate exceptional performance in research assays. The ELISA assay on the left highlights a dose-dependent response using 0.2 µg of human TNF-α per well, confirming strong binding activity and neutralizing capabilities of the biosimilar.
Meet Some of the Genie Team!
At Assay Genie, we're here to help every step of the way. Whether you need guidance choosing the right product, updates on your order, or expert support after your purchase, we've got you covered.
FAQs & Citations
Research-grade biosimilars are laboratory-produced proteins that are designed to mimic the structure and function of approved biologic drugs. They are used in preclinical studies, assay development, and other non-clinical applications.
Research-grade biosimilars are intended for laboratory and research purposes only. They are not subject to the same regulatory scrutiny as therapeutic biosimilars, which must undergo clinical trials and approval processes for patient use.
No, research-grade biosimilars are designed to be similar in structure and function to reference biologics but are not identical. They are primarily used for assay development, drug screening, and in vitro/in vivo research.
They may be produced in similar systems (e.g., CHO cells, E. coli, yeast), but there can be differences in post-translational modifications, glycosylation patterns, or impurities.
Quality is assessed through purity analysis (SDS-PAGE, HPLC, Mass Spectrometry), bioactivity assays, and binding affinity tests (e.g., ELISA, SPR, BLI).
- Preclinical drug screening
- Assay development and validation (e.g., ELISA, Western Blot, Flow Cytometry)
- Mechanism of action studies
- Comparative studies against reference biologics
Yes, they can be used in in vivo models to study pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and efficacy before moving to clinical-grade biosimilars.
Product | Author | Citation |
|---|---|---|
Bikoriman et al. | ||
Leane et al. | ||
Rohani et al. | ||
Calvo et al. | ||
Turley et al. | ||
Wang et al. |