Bilirubin Assay Kit - Information
Assay Genie's bilirubin assay kit is designed to measure bilirubin in blood specimen in 96-well or cuvette formats. The improved Jendrassik-Grof method utilizes the reaction of bilirubin with diazotized sulfanilic acid, in which a red colored product is formed. The intensity of the color, measured at 510-550nm, is an accurate measure of the bilirubin level in the sample. Total bilirubin is assessed using caffeine benzoate to split bilirubin from the unconjugated bilirubin protein complex.
Applications
For quantitative determination of bilirubin and evaluation of drug effects on bilirubin metabolism.
Bilirubin Assay Kit - Key Features
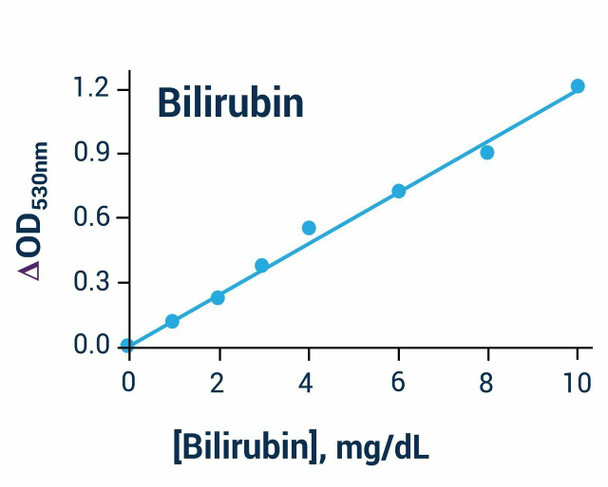
- Sensitive and accurate. Detection limit 0.16 mg/dL bilirubin in 96-well plate assay.
- Simple and high-throughput. The procedure involves addition of a single working reagent and incubation for 10 min. Can be readily automated as a high-throughput assay in 96-well plates for thousands of samples per day.
Bilirubin Assay Kit - Data Sheet | |
| Kit Includes | Reagent A: 30 mL Reagent B: 10 mL Reagent C: 30 mL Saline: 50 mL Calibrator: 2 mL (equivalent to 5 mg/dL Bilirubin) |
| Kit Requires | Pipeting devices and accessories, 96-well plates and plate reader |
| Method of Detection | OD530nm |
| Detection Limit | 0.16 mg/dL |
| Samples | Serum |
| Species | All |
| Protocol Length | 10 min |
| Size | 180 tests |
| Storage | Store all reagents at 4 °C |
| Shelf Life | 12 months |
More Details
BILIRUBIN is one of the degradation products of hemoglobin formed when red blood cells die. Bilirubin exists in the insoluble unconjugated form (also indirect bilirubin), or soluble glucuronide conjugated form bilirubin (also direct bilirubin). Conjugated bilirubin moves into the bile canaliculi of the liver and then to the gall bladder. When stimulated by eating, bile (including the conjugated bilirubin) is excreted into the small intestine, where bilirubin is converted into urobilinogen. Bilirubin is a key diagnostic indicator. High levels of bilirubin result when too much hemoglobin is broken down or the removal of bilirubin does not function properly. The accumulation of bilirubin in the body causes jaundice. Simple and automation-ready procedures for quantitative determination of bilirubin find wide applications in research and drug discovery.