Description
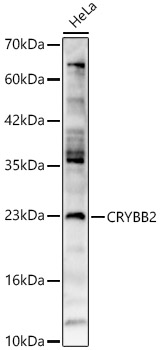
CRYBB2 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (CAB5573)
The Beta-Crystallin B2 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB5573) is a powerful tool for researchers studying Beta-Crystallin B2, a protein known for its role in maintaining lens transparency in the eye. This antibody, generated in rabbits, exhibits high specificity for human samples and has been validated for use in Western blot applications. By targeting the Beta-Crystallin B2 protein, this antibody allows for precise detection and analysis in a variety of cell types, making it an essential tool for investigations in ophthalmology and vision research.
Beta-Crystallin B2 is a vital component of the lens structure, contributing to its clarity and refractive properties. Mutations in the Beta-Crystallin B2 gene have been associated with cataract formation and other lens abnormalities, emphasizing the importance of understanding its function in maintaining ocular health. By studying Beta-Crystallin B2 using this antibody, researchers can gain insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying lens development and diseases affecting visual acuity.
| Product Name: | CRYBB2 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody |
| SKU: | CAB5573 |
| Size: | 20uL, 100uL |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Reactivity: | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-205 of human CRYBB2 (NP_000487.1). |
| Sequence: | MASD HQTQ AGKP QSLN PKII IFEQ ENFQ GHSH ELNG PCPN LKET GVEK AGSV LVQA GPWV GYEQ ANCK GEQF VFEK GEYP RWDS WTSS RRTD SLSS LRPI KVDS QEHK IILY ENPN FTGK KMEI IDDD VPSF HAHG YQEK VSSV RVQS GTWV GYQY PGYR GLQY LLEK GDYK DSSD FGAP HPQV QSVR RIRD MQWH QRGA FHPS N |
| Tested Applications: | WB ELISA |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB,1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Synonyms: | CCA2; CRYB2; CRYB2A; CTRCT3; D22S665; CRYBB2 |
| Positive Sample: | HeLa,Mouse eye,Rat eye |
| Conjugate: | Unconjugated |
| Calculated MW: | 23kDa |
| Observed MW: | 25kDa |
Crystallins are separated into two classes: taxon-specific, or enzyme, and ubiquitous. The latter class constitutes the major proteins of vertebrate eye lens and maintains the transparency and refractive index of the lens. Since lens central fiber cells lose their nuclei during development, these crystallins are made and then retained throughout life, making them extremely stable proteins. Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families; beta and gamma crystallins are also considered as a superfamily. Alpha and beta families are further divided into acidic and basic groups. Seven protein regions exist in crystallins: four homologous motifs, a connecting peptide, and N- and C-terminal extensions. Beta-crystallins, the most heterogeneous, differ by the presence of the C-terminal extension (present in the basic group, none in the acidic group). Beta-crystallins form aggregates of different sizes and are able to self-associate to form dimers or to form heterodimers with other beta-crystallins. This gene, a beta basic group member, is part of a gene cluster with beta-A4, beta-B1, and beta-B3. A chain-terminating mutation was found to cause type 2 cerulean cataracts.
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Gene ID: | 1415 |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide,50% glycerol,pH7.3. |