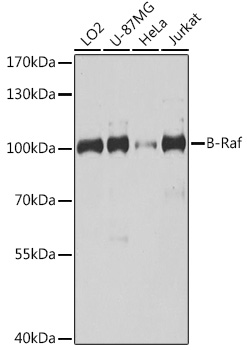
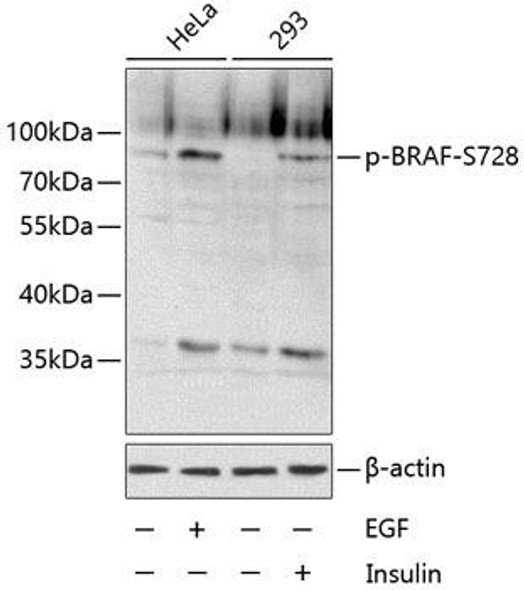
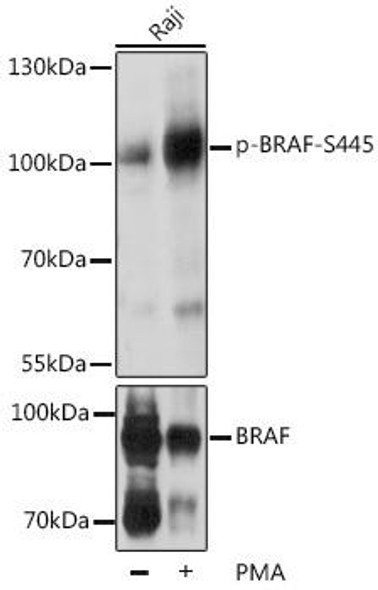
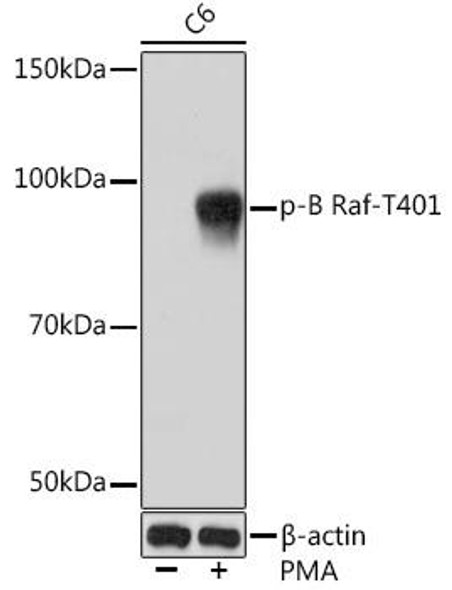
Description
B-Raf Polyclonal Antibody (CAB21612)
The B-RAF Polyclonal Antibody (CAB21612) is a valuable tool for researchers studying the B-RAF protein, a key player in cell signaling pathways and cancer development. This antibody, produced in rabbits, exhibits high reactivity with human samples and is validated for use in Western blot applications.B-RAF is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is mutated in various cancers, making it a promising target for cancer therapy. By detecting and analyzing B-RAF protein levels in different cell types, this antibody is essential for investigating the role of B-RAF in cancer progression and drug resistance mechanisms.
Furthermore, understanding the function of B-RAF is critical for developing targeted therapies and personalized medicine strategies for cancer treatment. With its specificity and sensitivity, the B-RAF Polyclonal Antibody is a valuable asset for researchers in the fields of oncology and cell signaling research.
| Product Name: | B-Raf Polyclonal Antibody |
| SKU: | CAB21612 |
| Size: | 20uL, 100uL |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 350-449 of human B-Raf (NP_004324.2). |
| Sequence: | DEDH RNQF GQRD RSSS APNV HINT IEPV NIDD LIRD QGFR GDGG STTG LSAT PPAS LPGS LTNV KALQ KSPG PQRE RKSS SSSE DRNR MKTL GRRD SSDD |
| Tested Applications: | WB ELISA |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB,1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Synonyms: | NS7; B-raf; BRAF1; RAFB1; B-RAF1; BRAF-1; B-Raf |
| Conjugate: | Unconjugated |
| Cellular Localization: | Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus. |
| Calculated MW: | 84kDa |
| Observed MW: | Refer to figures |
This gene encodes a protein belonging to the RAF family of serine/threonine protein kinases. This protein plays a role in regulating the MAP kinase/ERK signaling pathway, which affects cell division, differentiation, and secretion. Mutations in this gene, most commonly the V600E mutation, are the most frequently identified cancer-causing mutations in melanoma, and have been identified in various other cancers as well, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma, colorectal cancer, thyroid carcinoma, non-small cell lung carcinoma, hairy cell leukemia and adenocarcinoma of lung. Mutations in this gene are also associated with cardiofaciocutaneous, Noonan, and Costello syndromes, which exhibit overlapping phenotypes. A pseudogene of this gene has been identified on the X chromosome.
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Gene ID: | 673 |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide,50% glycerol,pH7.3. |