Description
ATXN1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (CAB6217)
The Ataxin-1 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB6217) is a valuable tool for researchers studying Ataxin-1, a protein involved in neurodegenerative disorders such as Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1). The antibody, produced in rabbits, exhibits high specificity and sensitivity for detecting Ataxin-1 in human samples, making it ideal for use in various research techniques, including Western blot analysis.Ataxin-1 is known to play a crucial role in the development of SCA1, a genetic disorder characterized by progressive loss of coordination and movement.
By targeting Ataxin-1, researchers can better understand the mechanisms underlying SCA1 and potentially identify new therapeutic strategies for treating the disease. The Ataxin-1 Polyclonal Antibody provides a reliable tool for studying Ataxin-1 expression and function in both normal and diseased tissues, advancing our knowledge of neurodegenerative disorders.
| Product Name: | ATXN1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody |
| SKU: | CAB6217 |
| Size: | 20uL, 100uL |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Reactivity: | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 586-815 of human ATXN1 (NP_001121636.1). |
| Sequence: | ELKK VEDL KTED FIQS AEIS NDLK IDSS TVER IEDS HSPG VAVI QFAV GEHR AQVS VEVL VEYP FFVF GQGW SSCC PERT SQLF DLPC SKLS VGDV CISL TLKN LKNG SVKK GQPV DPAS VLLK HSKA DGLA GSRH RYAE QENG INQG SAQM LSEN GELK FPEK MGLP AAPF LTKI EPSK PAAT RKRR WSAP ESRK LEKS EDEP PLTL PKPS LIPQ EVKI CIEG RSNV GK |
| Tested Applications: | WB ELISA |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB,1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Synonyms: | ATX1; SCA1; D6S504E; ATXN1 |
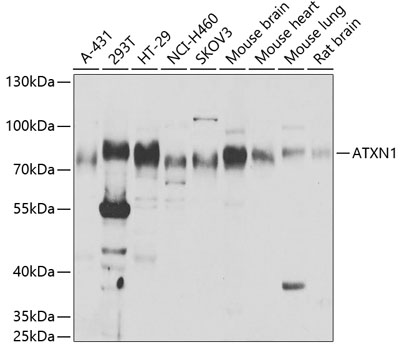
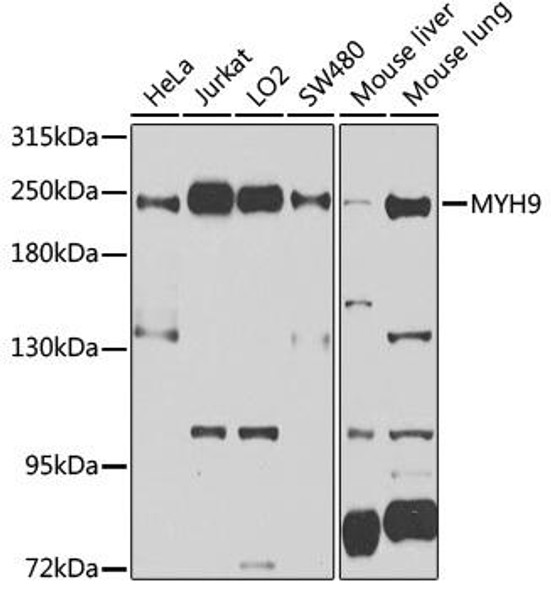
| Positive Sample: | A-431,293T,HT-29,NCI-H460,SKOV3,Mouse brain,Mouse heart,Mouse lung,Rat brain |
| Conjugate: | Unconjugated |
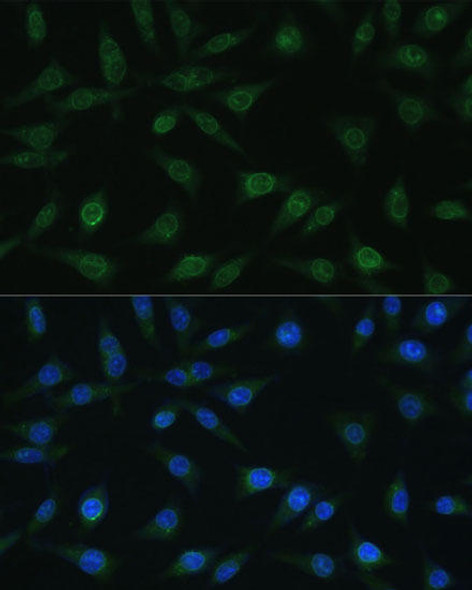
| Cellular Localization: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus. |
| Calculated MW: | 87kDa |
| Observed MW: | 87kDa |
The autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxias (ADCA) are a heterogeneous group of neurodegenerative disorders characterized by progressive degeneration of the cerebellum, brain stem and spinal cord. Clinically, ADCA has been divided into three groups: ADCA types I-III. ADCAI is genetically heterogeneous, with five genetic loci, designated spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6, being assigned to five different chromosomes. ADCAII, which always presents with retinal degeneration (SCA7), and ADCAIII often referred to as the `pure' cerebellar syndrome (SCA5), are most likely homogeneous disorders. Several SCA genes have been cloned and shown to contain CAG repeats in their coding regions. ADCA is caused by the expansion of the CAG repeats, producing an elongated polyglutamine tract in the corresponding protein. The expanded repeats are variable in size and unstable, usually increasing in size when transmitted to successive generations. The function of the ataxins is not known. This locus has been mapped to chromosome 6, and it has been determined that the diseased allele contains 40-83 CAG repeats, compared to 6-39 in the normal allele, and is associated with spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, with one variant encoding multiple distinct proteins, ATXN1 and Alt-ATXN1, due to the use of overlapping alternate reading frames.
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Gene ID: | 6310 |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide,50% glycerol,pH7.3. |