Atezolizumab: Unveiling the Role of Anti-PD-L1 in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Atezolizumab
What is Atezolizumab?
Atezolizumab is an anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody used in immunotherapy to treat various cancers by enhancing the immune system's ability to attack tumors.
What is the mechanism of action for Atezolizumab?
Atezolizumab blocks the interaction between PD-L1 and PD-1, restoring T-cell activity and promoting anti-tumor immunity.
What are the clinical applications of Atezolizumab?
It is approved for cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), and urothelial carcinoma, among others.
1.) Understanding Atezolizumab
Atezolizumab, marketed under the name Tecentriq, is a pioneering immunotherapy developed by Roche. As a PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitor, it represents a significant advancement in oncology, offering new treatment avenues for patients with difficult-to-treat cancers. By targeting the PD-L1 protein on tumor cells and immune cells, Atezolizumab reactivates T-cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Its versatile applications in treating solid tumors and hematologic malignancies make it a cornerstone of modern immuno-oncology.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Atezolizumab
Atezolizumab works by blocking the PD-L1 protein’s interaction with PD-1 and B7.1 receptors on T-cells. This blockade prevents immune suppression, allowing T-cells to remain active against cancer cells. Its specificity for PD-L1—without affecting PD-1—helps maintain a balanced immune response, reducing potential immune-related side effects. This mechanism complements other therapies, such as VEGF inhibitors like bevacizumab, making combination regimens a promising strategy for enhancing efficacy.
3.) Clinical Applications of Atezolizumab
4.) Advancing Research on Atezolizumab with Biosimilars
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a highly similar alternative to an original biologic drug, offering equivalent safety, purity, and potency. In research, biosimilars are invaluable for studying drug mechanisms, testing combinations, and expanding accessibility.
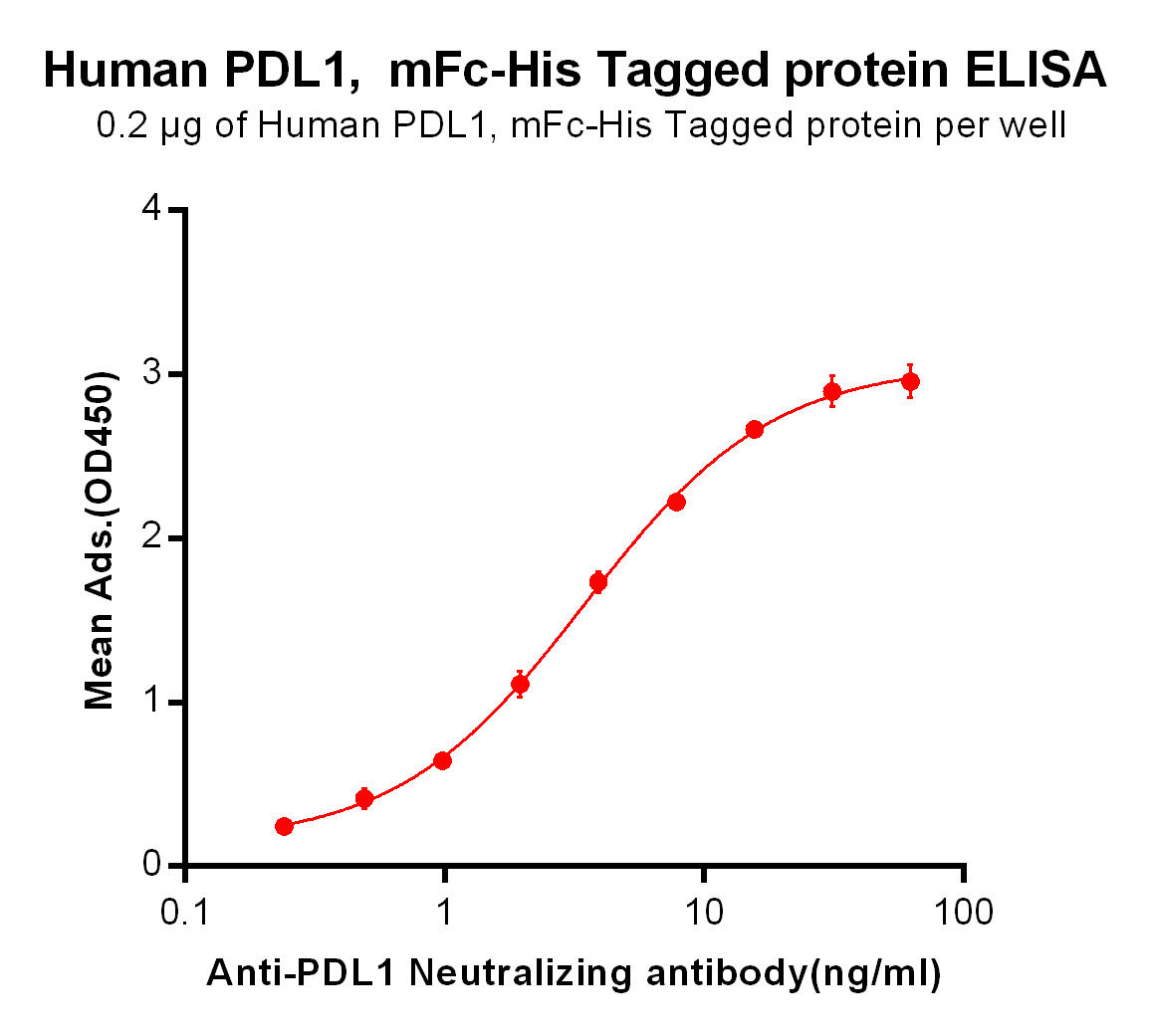
| Atezolizumab (Anti-PDL1) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | PD-L1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Atezolizumab Biosimilar: A Research Tool
Our Atezolizumab biosimilar enables researchers to investigate PD-L1 pathways efficiently and cost-effectively. This research-use-only product mirrors the binding and activity of the original, facilitating detailed studies on immunotherapy mechanisms.
Benefits for Research:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the financial barriers to accessing cutting-edge research tools.
- High Fidelity: Maintains the specificity and functional properties of the original drug, ensuring accurate experimental results.
- Versatility: Suitable for a variety of research applications, from preclinical trials to in vitro studies.
Note: This biosimilar is strictly for research purposes and not intended for clinical or therapeutic use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

Wrote by Shanza Riaz
Recent Posts
-
Tigatuzumab Biosimilar: Harnessing DR5 for Targeted Cancer Therapy
Tigatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting death receptor 5 (DR5), a member of the …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab Biosimilar: Advancing CD52-Targeted Therapy
Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD52, a glycoprotein highly expressed on …17th Dec 2025 -
Enavatuzumab Biosimilar: Advancing TWEAKR-Targeted Therapy in Cancer
Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting TWEAK receptor (TWEAKR, also known as F …17th Dec 2025




