APOL6 Antibody (PACO19319)
- SKU:
- PACO19319
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Applications:
- ELISA
- IHC
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Conjugation:
- Unconjugated
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | APOL6 Antibody (PACO19319) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO19319 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:2000-1:5000, IHC:1:50-1:200 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide of human APOL6 |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | -20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol |
| Purification Method: | Antigen affinity purification |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
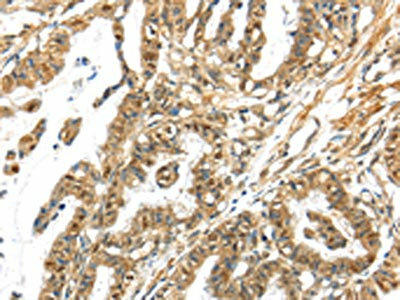 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human thyroid cancer tissue using PACO19319(APOL6 Antibody) at dilution 1/60, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: x200). |
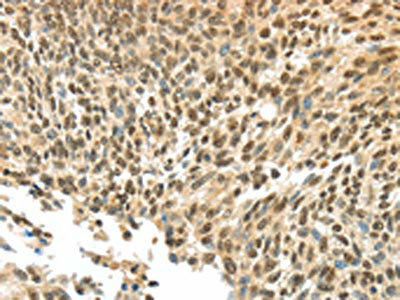 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human tonsil tissue using PACO19319(APOL6 Antibody) at dilution 1/60, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: x200). |
| Background: | This gene is a member of the apolipoprotein L gene family. The encoded protein is found in the cytoplasm, where it may affect the movement of lipids or allow the binding of lipids to organelles. Widely expressed; highly expressed in the uterus, fetal brain and spinal cord, also detected in heart, liver, lung, colon, spleen, thymus, prostate, placenta, adrenal gland, salivary and mammary gland. |
| Synonyms: | apolipoprotein L, 6 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | |
| UniProt Protein Details: | |
| NCBI Summary: | |
| UniProt Code: | Q9BWW8 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 13449281 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 80830 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_085144.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9BWW8,Q5R3S1, Q658J1, Q8IXX6, Q9UGG1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9BWW8 |
| Molecular Weight: | 38,128 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | apolipoprotein L6 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | apolipoprotein L, 6 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | APOL6 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | APOLVI; APOL-VI |
| NCBI Protein Information: | apolipoprotein L6; apolipoprotein L-VI |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Apolipoprotein L6 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Apolipoprotein L-VI |
| Protein Family: | Apolipoprotein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | APOL6 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | APOL6_HUMAN |
| Antibodies |
| APOL6 Antibody (PACO01778) |
| Secondary Antibody |
| Anti-HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Antibody (CABS014) |
| Recommended Products |
| Anti-FITC Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Antibody (CABS011) |
| Anti-HRP-conjugated Beta Actin Antibody (CABC028) |







