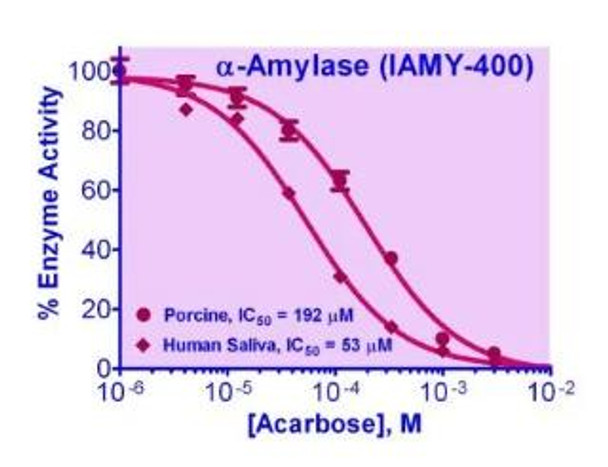
AMYLASE belongs to the family of glycoside hydrolase enzymes that break down starch into glucose molecules by acting on α-1,4-glycosidic bonds. The α-amylases (EC 3.2.1.1) cleave at random locations on the starch chain, ultimately yielding maltotriose and maltose, glucose, and “limit dextrin” from amylose and amylopectin. In mammals, α-amylase is a major digestive enzyme. Increased enzyme levels in humans are associated with salivary trauma, mumps due to inflammation of the salivary glands, pancreatitis, and renal failure.Simple, direct, and automation-ready procedures for measuring α-amylase inhibition are highly desirable in Research and Drug Discovery. BioAssay Systems’ QuantiFluo™ α-Amylase Inhibitor Screening Kit utilizes fluorescence polarization (FP) to screen for potential α-amylase inhibitors. In this assay, α-amylase cleaves a fluorescent amylose substrate. The decrease in FP is directly proportional to the α-amylase activity in the sample. Inhibition is therefore determined by the increase in FP (λex/em = 485/520 nm).