Alcohol dehydrogenase Activity Assay Kit - Information
Assay Genie's non-radioactive, colorimetric ADH assay is based on the reduction of the tetrazolium salt MTT in a NADH-coupled enzymatic reaction to a reduced form of MTT which exhibits an absorption maximum at 565 nm. The increase in absorbance at 565 nm is directly proportional to the enzyme activity.
Applications
For quantitative determination of alcohol dehydrogenase activity and evaluation of drug effects on its metabolism.
Alcohol dehydrogenase Activity Assay Kit - Key Features
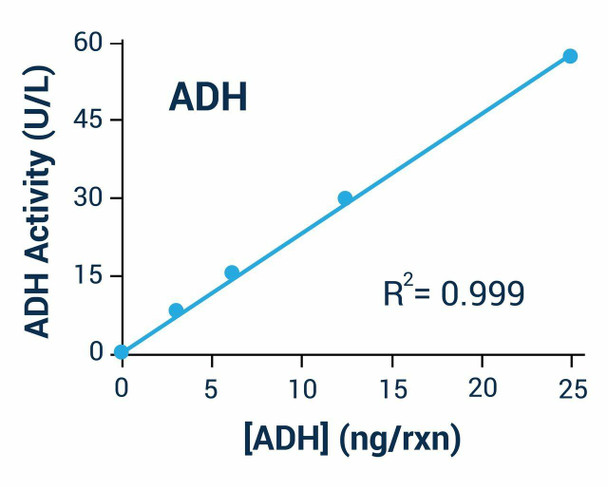
- Fast and sensitive. Linear detection range (20 sample): 0.4 to 80 U/L for 30 min reaction. Detection Limit of 0.1 U/L for 120 min reaction.
- Convenient and high-throughput. Homogeneous "mix-incubate-measure" type assay. Can be readily automated on HTS liquid handling systems for processing thousands of samples per day.
Alcohol dehydrogenase Activity Assay Kit - Data Sheet | |
| Kit Includes | Assay Buffer: 10 mL Diaphorase : 120 uL NAD Solution: 1 mL Calibrator: 1.5 mL MTT Solution: 1.5 mL Substrate: 1 mL 10% Ethanol |
| Kit Requires | Pipetting devices and accessories (e.g. multi-channel pipettor), clear flat- bottom 96-well plates, centrifuge tubes and plate reader. |
| Method of Detection | OD565nm |
| Detection Limit | 0.4 U/L |
| Samples | Biological (e.g. plasma, serum, urine, tissue and culture media) |
| Species | All |
| Protocol Length | 30 min |
| Size | 100 tests |
| Storage | Store all components at -20°C upon receiving |
| Shelf Life | 6 months |
More Details
ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE (ADH) is an oxidoreductase which catalyzes the interconversion of alcohols and aldehydes or ketones. ADH is important in humans and other organisms for the break down of alcohols which may otherwise be toxic. In yeast and some bacteria, ADHs catalyze the opposite reaction and produce alcohol as part of fermentation.