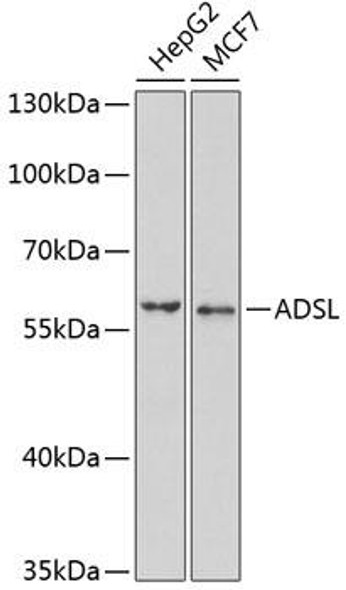
Description
ADSL Monoclonal Antibody [PAT16C10AT] (CPAB0225)
The ADSL Antibody (CPAB0225) offered by AssayGenie is a polyclonal antibody designed for research involving Adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL), an enzyme that plays a critical role in the purine nucleotide biosynthesis pathway. This antibody, raised in rabbits, is highly reactive with human and mouse samples and is validated for use in various applications including Western blot and immunohistochemistry.ADSL is a key enzyme in the de novo purine synthesis pathway and is essential for the production of purine nucleotides, which are crucial for DNA and RNA synthesis.
Mutations in the ADSL gene are associated with rare inherited disorders such as Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency, which results in neurological and developmental abnormalities.Research involving the ADSL Antibody can provide valuable insights into purine metabolism, nucleotide synthesis, and the molecular mechanisms underlying ADSL-related disorders. This antibody enables the detection and analysis of ADSL protein expression in different cell types and tissues, making it a valuable tool for studies in biochemistry, genetics, and molecular biology.
| Product Name: | ADSL Antibody |
| Product Sku: | CPAB0225 |
| Size: | 5μg |
| Host Species: | Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Anti-human ADSL mAb, is derived from hybridization of mouse F myeloma cells with spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized with a recombinant human ADSL protein 1-484 amino acids purified from Ecoli. |
| Clone: | PAT16C10AT. |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow Cytometry |
| Purification Method: | ADSL antibody was purified from mouse ascitic fluids by protein-A affinity chromatography. |
| Isotype: | IgG1 |
| Background: | Adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL) is an enzyme which converts adenylosuccinate to AMP and fumarate as part of the purine nucleotide cycle. ADSL is involved in both de novo synthesis of purines and formation of adenosine monophosphate from inosine monophosphate. ADSL catalyzes 2 reactions in AMP biosynthesis: the removal of a fumarate from succinylaminoimidazole carboxamide (SAICA) ribotide to yield aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide (AICA) and removal of fumarate from adenylosuccinate to yield AMP. Defects in the ADSL are the cause of adenylosuccinase deficiency (ADSL deficiency). ADSL deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder distinguished by the accumulation in the body fluids of succinylaminoimidazole-carboxamide riboside (SAICA-riboside) and succinyladenosine (S-Ado). Adenylosuccinase deficiency results in succinylpurinemic autism, psychomotor retardation, and in some cases, growth retardation associated with muscle wasting and epilepsy. |
| Synonyms: | Adenylosuccinate lyase, ASL, Adenylosuccinase, ASase, ADSL, AMPS. |
| Storage Buffer: | For periods up to 1 month store at 4°C, for longer periods of time, store at -20°C. Prevent freeze thaw cycles. |