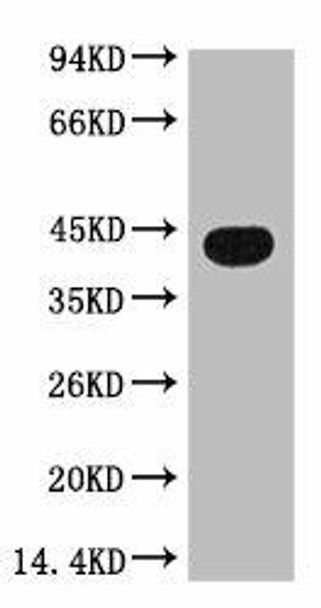
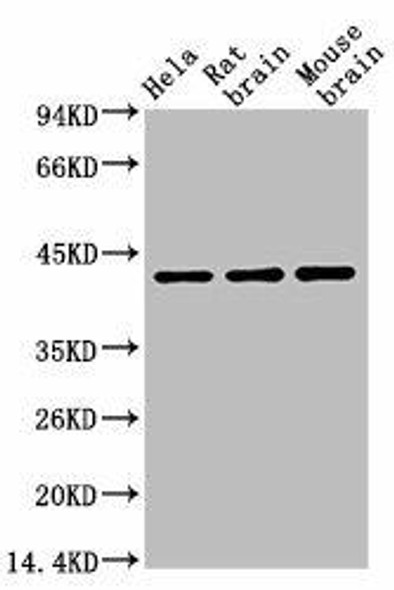
Description
Anti-ACTB Antibody (MACO0090)
The ACTB Monoclonal Antibody (MACO0090) is a vital tool for researchers studying beta-actin, a highly conserved protein essential for cell structure and motility. This antibody, produced through a hybridoma technique, demonstrates high specificity and sensitivity for detecting beta-actin in various experimental applications, such as Western blotting and immunofluorescence.Beta-actin, a key component of the cytoskeleton, is involved in numerous cellular processes, including cell migration, adhesion, and division. Dysregulation of beta-actin expression or function has been linked to various diseases, making it a focus of interest in cancer research, developmental biology, and cell biology studies.
By using the ACTB Monoclonal Antibody, researchers can accurately quantify beta-actin levels in different cell types and experimental conditions, providing valuable insights into the role of this protein in health and disease. This antibody is a valuable tool for advancing our understanding of cellular dynamics and identifying potential therapeutic targets for a range of medical conditions.
| Product Name: | Anti-ACTB Antibody |
| Product Sku: | MACO0090 |
| Size: | 50ug |
| Host Species: | Mouse |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, WB |
| Recommended Dilutions: | WB:1:500-1:5000 |
| Species Reactivity: | Zebrafish |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic Peptide |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | PBS, pH 7.4, containing 0.02% sodium azide as Preservative and 50% Glycerol. |
| Purification Method: | The antibody was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen. |
| Clonality: | Monoclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
| Background: | |
| Synonyms: | ACTB; Actin, cytoplasmic 1; Beta-actin |
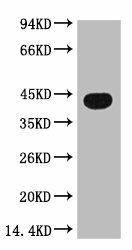 | Western blot analysis of Zebrafish skeletal muscle, diluted at 1:3000. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Function: Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Subunit structure: Polymerization of globular actin (G-actin) leads to a structural filament (F-actin) in the form of a two-stranded helix. Each actin can bind to 4 others. Identified in a mRNP granule complex, at least composed of ACTB, ACTN4, DHX9, ERG, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPAB, HNRNPD, HNRNPL, HNRNPR, HNRNPU, HSPA1, HSPA8, IGF2BP1, ILF2, ILF3, NCBP1, NCL, PABPC1, PABPC4, PABPN1, RPLP0, RPS3, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPS8, RPS9, SYNCRIP, TROVE2, YBX1 and untranslated mRNAs. Component of the BAF complex, which includes at least actin (ACTB), ARID1A, ARID1B/BAF250, SMARCA2, SMARCA4/BRG1, ACTL6A/BAF53, ACTL6B/BAF53B, SMARCE1/BAF57 SMARCC1/BAF155, SMARCC2/BAF170, SMARCB1/SNF5/INI1, and one or more of SMARCD1/BAF60A, SMARCD2/BAF60B, or SMARCD3/BAF60C. In muscle cells, the BAF complex also contains DPF3. Found in a complex with XPO6, Ran, ACTB and PFN1. Component of the MLL5-L complex, at least composed of MLL5, STK38, PPP1CA, PPP1CB, PPP1CC, HCFC1, ACTB and OGT. Interacts with XPO6 and EMD. Interacts with ERBB2. Interacts with GCET2. Ref.11 Ref.12 Ref.15 Ref.22 Subcellular location: Cytoplasm cytoskeleton. Note: Localized in cytoplasmic mRNP granules containing untranslated mRNAs. Ref.17 Post-translational modification: ISGylated. Ref.13Oxidation of Met-44 by MICALs (MICAL1, MICAL2 or MICAL3) to form methionine sulfoxide promotes actin filament depolymerization. Methionine sulfoxide is produced stereospecifically, but it is not known whether the (S)-S-oxide or the (R)-S-oxide is produced By similarity. Involvement in Disease: Defects in ACTB are a cause of dystonia juvenile-onset (DYTJ) [ MIM:607371]. DYTJ is a form of dystonia with juvenile onset. Dystonia is defined by the presence of sustained involuntary muscle contraction, often leading to abnormal postures. DYTJ patients manifest progressive, generalized, dopa-unresponsive dystonia, developmental malformations and sensory hearing loss. Ref.23Defects in ACTB are the cause of Baraitser-Winter syndrome type 1 (BRWS1) [ MIM:243310]. A rare developmental disorder characterized by the combination of congenital ptosis, high-arched eyebrows, hypertelorism, ocular colobomata, and a brain malformation consisting of anterior-predominant lissencephaly. Other typical features include postnatal short stature and microcephaly, intellectual disability, seizures, and hearing loss. Ref.25 Miscellaneous: In vertebrates 3 main groups of actin isoforms, alpha, beta and gamma have been identified. The alpha actins are found in muscle tissues and are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. The beta and gamma actins coexist in most cell types as components of the cytoskeleton and as mediators of internal cell motility. Sequence similarities: Belongs to the actin family. |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes one of six different actin proteins. Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in cell motility, structure, and integrity. This actin is a major constituent of the contractile apparatus and one of the two nonmuscle cytoskeletal actins. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P60709 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 46397333 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 60 |
| NCBI Accession: | P60709.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P60709,P02570, P70514, P99021, Q11211, Q64316, Q75MN2 Q96B34, Q96HG5, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P60709 |
| Molecular Weight: | 67 KD |
| NCBI Full Name: | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | actin, beta |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ACTB |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | BRWS1; PS1TP5BP1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | actin, cytoplasmic 1; beta cytoskeletal actin; PS1TP5-binding protein 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Beta-actin |
| Protein Family: | Actin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ACTB |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ACTB_HUMAN |